Soybean Kernel Damage
Principal Soybean Kernel Damage
Badly Ground and/or weather damage
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans in which the seedcoats are discolored by ground or weather damage. The discoloration may be on one side or both sides.

Damaged by heat
Soybeans which have been damaged by heat shall be considered damaged but not heat damaged. It is often necessary to cross section whole soybeans to determine the extent of the damage.
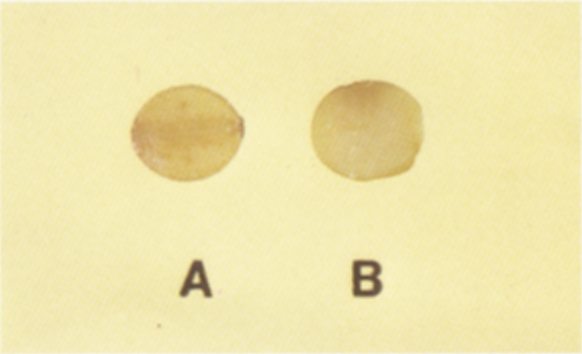
Frost damage (Green)
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which are discolored green in cross section.
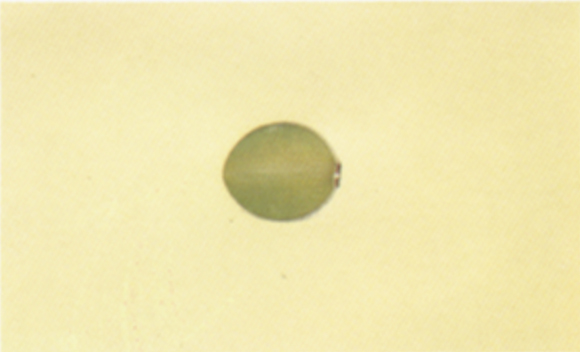
Heat damage
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which are materially discolored and damaged by heat. Often kernels need to be cross sectioned to determine the extent of the damage.
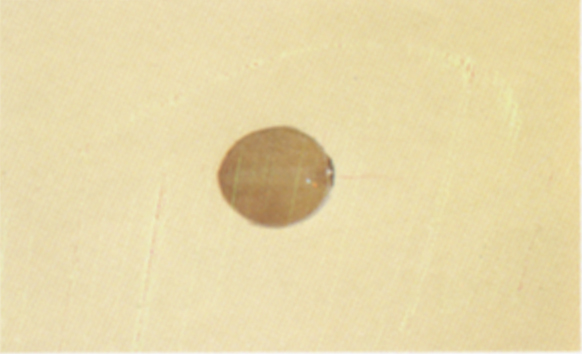
Frost damage (Waxy)
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which have a glassy or wax-like appearance.
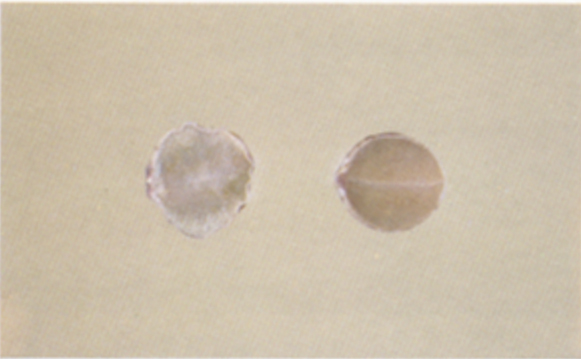
Immature Soybeans (Wafers)
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which are immature and have a thin, flat, wrinkled, or wafer-like appearance shall be cross sectioned. If there is “meat” left in the kernels and the “meat” is not otherwise damaged, the wafers shall be considered as sound kernels. Wafers with no “meat” shall be considered damaged.
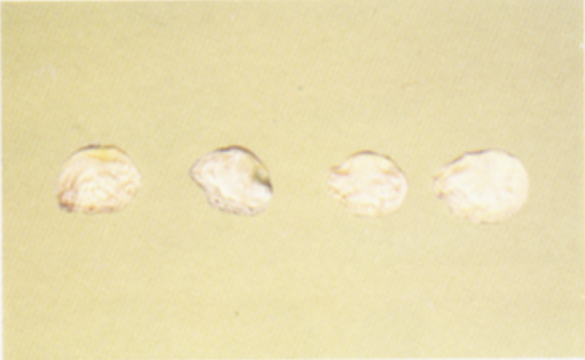
Mold Damage (pink)
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans that exhibit a pink discoloration caused by fungal activity. Soybeans that contain pink discoloration to the seed equal to or greater than the amount shown are considered damaged.

Badly Ground and/or weather damage (Gray/black)
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans with seedcoats that are discolored light gray to black. Soybeans that contain gray/black discoloration of the seedcoat equal to or greater than the amount shown are considered damaged.

Sprout damage
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which are sprouted with the sprout protruding.

Insect damage
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which bear evidence of boring or tunneling shall be considered damaged. Kernels which have been partially eaten by insects but are free from refuse, insects, or their forms of damage shall be considered sound.
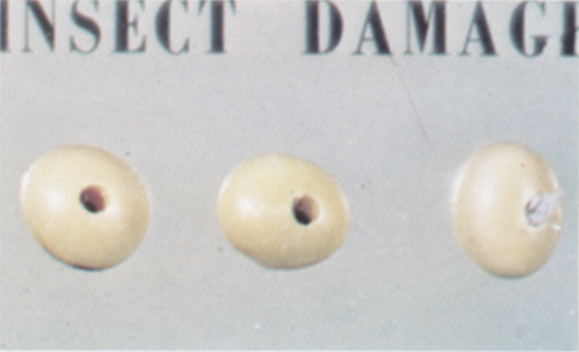
Insect stung
Soybeans and pieces of soybeans which show an indentation or discoloration on the seedcoat due to insect stings shall be considered damaged at the rate of one-fourth of the actual percentage.
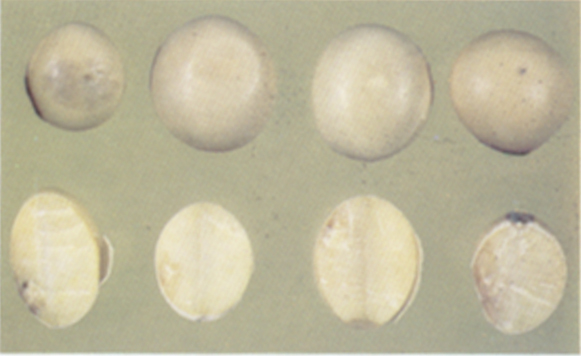
Mold damage
- Invaded by mold. Soybeans which are discolored; distorted; misshapen; or have splits, cracks, or fissures in the seedcoat which contain white to gray moldy growth.
- Surface mold. Soybeans with little or no apparent deterioration containing milky white or grayish crusty growth on 50% or more of the seedcoat.
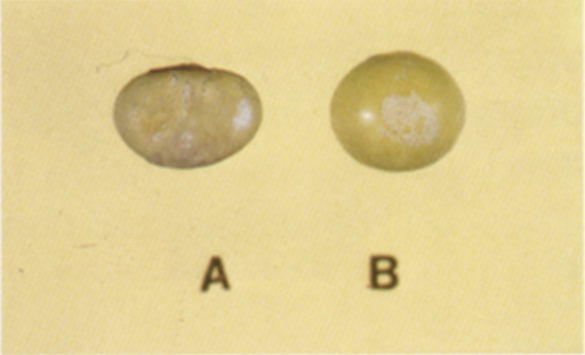
Purple mottled or stained
Soybeans which are discolored by the growth of a fungus; or by dirt; or by dirt-like substance, including non-toxic inoculants; or by other non-toxic substances.

Garlicky
Soybeans which contain 5 or more garlic bulblets in a 1,000-gram portion.
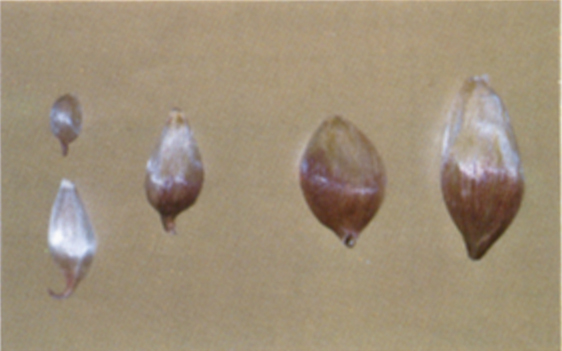
Infested
Soybeans that are infested with live weevils or other live insects injurious to stored grain. Soybeans will be considered infested if the representative sample, or lot as a whole (stationary) or component sample (continuous loading/unloading of ships and barges) contains two or more live weevils, or one live weevil and five or more other live insects injurious to stored grain, or ten or more other live insects injurious to stored grain.
Grade Requirements for Soybeans
Table 1. Maximum limits of damaged kernels.
| Grade | Minimum test weight per bushel (pounds) |
Splits (%) | Total (%) |
Heat damaged (%) |
Foreign material (%) |
Soybeans of other colors (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. No. 1 | 56 | 10 | 2 | 0.2 | 1 | 1 | |
| U.S. No. 2 | 54 | 20 | 3 | 0.5 | 2 | 2 | |
| U.S. No. 3 | 52 | 30 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| U.S. No. 4 | 49 | 40 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
U.S. Sample grade are soybeans that:
- Do not meet the requirements for the grades U.S. Numbers 1, 2, 3, or 4; or
- Contain 4 or more stones which have an aggregate weight in excess of 0.1 percent of the sample weight, 0 or more pieces of glass, 3 or more crotalaria seeds (Crotalaria spp.) 2 or more castor beans (Ricinus communis L.), 4 or more particles of an unknown foreign substance(s) or a commonly recognized harmful or toxic substance(s), 10 or more rodent pellets, bird droppings, or equivalent quantity of other animal filth per 1,000 grams of soybeans, or accumulation of 10 or more of these; or
- Have a musty, sour, or commercially objectionable foreign odor; or
- Are heating or otherwise of distinctly low quality.
Soybeans
Grain that consists of 50% or more whole or broken soybeans (Glycine Max [L.] Merr.) that will not pass through an 8/64 round-hole sieve and of not more than 10.0% other grains for which standards have been established under the Untied States Grain Standards Act.
Definition of other Terms
Classes. There are two classes for soybeans: yellow soybeans and mixed soybeans.
Yellow Soybeans . Soybeans that have yellow or green seedcoats and which in cross section are yellow or have a yellow tinge, and may not include more than 10% soybeans of other colors.
Mixed Soybeans. Soybeans that do not meet the requirements of the class yellow soybeans.
Soybeans of Other Colors. Soybeans that have green, black, brown, or bicolored seedcoats. Soybeans that have green seedcoats will also be green in cross section. Bicolored soybeans will have seedcoats to two colors, one of which is brown or black, with the brown or black color covering 50% of the seedcoats. The hilum of a soybean is not considered a part of the seedcoat for this determination.
Foreign Material. All matter that passes through an 8/64 round-hole sieve and all matter other than soybeans remaining in the sieved sample after sieving.
Splits. Soybeans with more than 1/4 of the bean removed and that are not damaged.
Jeff Edwards
