Managing Persistently Infected Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in Beef Cattle (PI-BVDV)
Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV) is a contributor (along with others) to what is known as “shipping fever,” a complex or bovine respiratory disease (BRD). This virus may also produce enteric disease (diarrhea) and reproductive disease like abortion and stillbirth. Cattle can be infected for their entire life and spread the disease to herd mates. These animals are referred to as persistently infected (PI). Tests are available to help identify these PI animals and remove them from the herd to prevent the spread of BVDV.
Persistently Infected Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (PI-BVDV)
PI animals are particularly harmful to cattle herds; as they may show no clinical signs of the disease, yet shed the virus continuously to surrounding animals. Both acutely infected (inapparent) and PI calves transmit the virus through secretions such as feces, nasal discharge, tears, saliva, urine, milk and semen. BVDV may also be transmitted during examination or palpation of the reproductive tract when gloves or sleeves are not changed between animals. Needles also can transfer the virus from animal to animal. The virus may survive several days in cool environments and be transferred from tools such as nose tongs, halters and other tools, if not properly sanitized.
Persistently infected calves acquire BVDV in utero during gestation. Infection of the calf in utero is the only way to become a PI animal. If a cow is infected at the time of fertilization, conception rates may be decreased. If the fetus is infected between zero days to 45 days of gestation, it will result in fetal death. A fetus infected between 30 days and 125 days of gestation may be PI. If it does survive, it will be born persistently infected. If the fetus is infected after 120 days, the calf may be aborted, stillborn, have congenital defects, be born weak or may be born as a live normal calf. Few cows with infected fetuses are themselves PI (5 percent or less); the majority of cows are acutely infected with the disease during gestation, but recover.
Transient (acute) infection (TI)
- Short term (weeks)
- Acquired after birth
- TI cattle become immune and clear virus
- More than 95 percent of BVD infections are TI
- TI cattle minor source of virus spread in herd
Persistent (chronic) infection (“PI”)
- Life-long infection
- Acquired in utero — only fetal infection results in BVD-PI
- PI cattle never become immune
- Less than 5 percent of BVD infection are PI
- PI cattle major source of virus spread in herd
- More than 90 percent of BVD-PI calves are born from normal dams (no prior BVDV exposure)
Clinical Signs or Visible Symptoms
Clinical signs of BVDV are highly variable. They can range from no clinical indication of infection to death. It can also negatively affect reproduction and fetal development in breeding females. Acute respiratory infection commonly occurs. This is indicated by loss of appetite and fever followed by discharge from the nose and eyes. This form of disease can last from 10 days to more than 14 days and may not be fatal. Reproductive losses from BVDV in the herd are not as quickly recognized. Low pregnancy rates, abortions, low birth weights, poor health or increased calf loss from birth to weaning are possible indications of a BVDV reproductive problem. Finally, enteric diseases such as diarrhea or bloody diarrhea (mucosal disease) are less commonly reported conditions occurring with BVDV infections.
Controlling BVDV
Biosecurity
Maintaining a closed herd or testing outside animals prior to purchase will aid in preventing BVDV. Good recordkeeping and animal identification strategies are an important initial consideration for successful biosecurity. All animals entering the breeding herd should be tested negative for BVDV and isolated for 30 days to ensure animals remain healthy. Testing and removal of BVDV-PI calves must occur before exposure of breeding females to bulls or before artificial insemination as a preventative measure. This includes bulls, females and any embryo recipients. If a female is pregnant, she should test negative and her newborn calf also should test negative. Most cows delivering a PI calf usually test negative themselves, however, they may be acutely infected and could deliver a PI calf. The untested breeding herd should be separated from stocker calves. Stocker calves of unknown origin may either be PI themselves or acutely infected, thus shed virus to the females. Animals entering bull test stations are often required to be tested for PI BVDV status before entry.
Testing
Testing cattle can be a valuable resource to eliminate PI-BVDV cattle from your herd. Several laboratories test for BVDV and offer variety of options to identify PI animals creating confusion for the producer. The best testing strategy for BVDV may be dependent upon the producer and type of cattle. Consult with a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate testing procedure for your herd. For most cow-calf producers and seed stock operations, an individual animal test is warranted to reduce the possibility of false negative tests.
These tests will frequently require a tissue sample from the top of the ear (ear notch), placed in a tube and labeled with proper animal ID. The testing laboratory will provide guidelines to appropriately submit test samples. Some laboratories may need fresh samples, whereas others may need formalin-fixed tissues. Fresh samples need to be placed on ice or refrigerated as soon as possible after collecting. If fresh tissues are needed, proper safety precautions for formalin-fixed tissues should be followed. Ear notch instruments used to collect the tissue sample need to be disinfected between animals according to laboratory instructions to prevent cross contamination of samples and maintain accurate results.
Some test results may need to be confirmed by a second test method to distinguish acute (temporary) infection from true PI animals. Consider this when screening groups of animals, particularly when multiple animals are identified in initial screenings. Working with a veterinarian and laboratory diagnostician is critical in determining the testing and interpretation of results. When BVDV is found in a herd, multiple tests may be necessary for disease control.
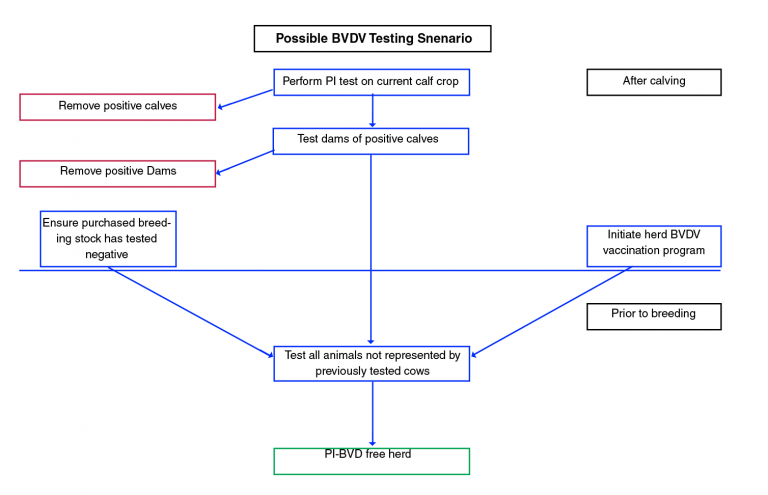
Testing all calves in the herd will be required. If a calf tests positive as a PI animal, the dam will need to be tested. All PI animals need to be removed from the herd immediately to prevent further spread of infection. Animals removed need to be disposed of in a proper manner and should not be sold, due to the risk of transmitting the disease to other farms or ranches. PI animals can be shipped directly to slaughter or finished in a quarantine facility away from other cattle to recover some of their value or euthanized. A possible testing scenario is outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1. A BVDV testing scenario. (Adapted from Sweiger, 2015.)
Vaccination
Implementing a biosecurity plan and testing regimen will remove all positive animals; the final phase of controlling BVDV is adequate vaccination. The minimum protection to consider for vaccination is annual immunization for BVDV. A local veterinarian is a valuable resource for determining the vaccination program. BVDV vaccination can easily be incorporated into programs that also provide protection against other respiratory disease (IBR, BRSV, Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida) as well as reproductive disease (Leptospirosis, Campylobacter and Vibriosis).
Prevention
Prevention of BVDV requires implementation of a well-designed biosecurity plan developed by the producer and a veterinarian, testing of animals with appropriate removal of all positive animals and a well-designed preventive vaccination program.
Marketing Negative Tested Calves
Calves testing negative can be marketed as PI-BVDV free. Many auction markets require producers to fill out an affidavit and provide test results when the cattle are sold in a “previously tested” or “value added” manner. Buyers, however, do not always offer a premium when purchasing PI free cattle. Auction results reported by Superior Livestock Auction have observed premiums in only two of the last seven years. In 2012 and 2013, cattle tested negative for BVDV witnessed an increase in price over non-BVDV tested cattle of $2.42/cwt and $2.97/cwt, respectively. Testing for PI-BVDV calves is more valuable as a preventive measure in cow-calf herds, to remove positive animals and reduce financial losses due to BVDV.
Incidence and Economic Impact in Oklahoma
Since 2006, numerous instances of PI cattle were diagnosed in Oklahoma. The number of herds may be small, but the number of PI calves may vary from a few to several per herd. Research indicates that finding a positive animal may be relatively low, but if one is found, the likelihood of finding multiple animals is high and extremely detrimental to a cow-calf producer. Historically, failed biosecurity on the ranch and lack of testing of new females, including pregnant females with PI calves added risk.
Reproductive losses are the most expensive to cow/calf producers and difficult to measure. Some estimates of the BVDV outbreak in 1998 were as much as $400 per cow and worth substantially more with the dramatic increase in calf values recently. Impacts of BVDV in the feedlot have been measured in several studies during the last few years. Cattle entering the feedlot and test positive as PI-BVDV, may only represent 0.3 percent, but cattle exposed to a PI-BVDV calf increase its chance of respiratory disease by 43 percent, and 15.9 percent of all respiratory tract disease can be attributed to exposure to a PI positive animal at some point (Loneragan et al., 2005). Performance alone of exposed calves can result in losses of $88.26 per animal (Hessman et al., 2009). It is recommended that animals with aborted calves or young animals dying of varied clinical signs should be tested for PI status. The first clue of BVDV in the herd often comes from diagnostic laboratory testing for BVDV.
References
Academy of Veterinary Consultants. 2004. BVD Decision / Management Guidelines for Beef Cattle Veterinarians. Bov. Pract. 38(No. 1):105
Hessman, B.E., R.W. Fulton, D.B. Sjeklocha, T.A. Murphy, J.F. Ridpath, and M.E. Payton. 2009. Evaluation of economic effects and the health and performance of the general cattle population after exposure to cattle persistently infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus in a starter feedlot. Am J Vet Res. 70:73.
Loneragan, G. H., D. U. Thomson, D. L. Montgomery, G. L. Mason, and R. L. Larson. 2005. Prevalence, outcome, and health consequences associated with persistent infection with bovine viral diarrhea virus in cattle. JAVMA, Vol. 226, No. 4.
Sweiger, S. 2015. BVD Oklahoma Department of Agriculture and Cattle Stats Voluntary BVD Control Program. PPT.
The effects of health and management programs on the sale price of beef calves marketed through eight Superior Livestock video auction in 2014. Final Report, Superior Livestock.
United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service. Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus. December 2007.
United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service. Persistent Infection of Calves with Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus on U.S. Beef Cow-calf Operations. #551.0609. June 2009.
Gant Mourer, MS
Beef Value Enhancement Specialist
Robert W. Fulton, DVM, Ph D
Professor of Veterinary Pathobiology
Grant Rezabek, DVM
Oklahoma Animal Disease Diagnostic Laboratory
Chris Richards, PH D
Beef Extension Specialist
Barry Whitworth, DVM
Area Food Animal/Quality & Health Specialist