Wellness for Older Adults in Daily Life
The wellness of older adults becomes more important as this age group increases in size. In the United States, about 70 million people will be over the age of 65 in 2030. This group will represent about 20 percent of the total U.S. population by 2030. Presently, the focus of wellness for older adults focuses on physical health. This fact sheet focuses on wellness for older adults and a Whole-Person Wellness Model. It recommends how daily activities can contribute to overall health.
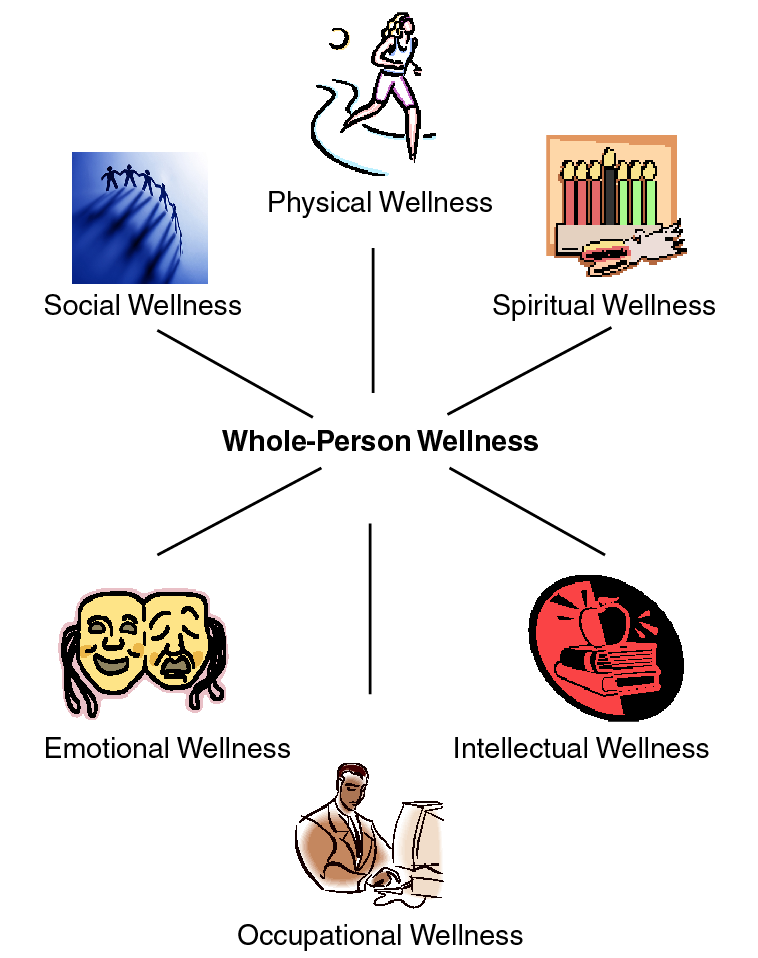
What is a Whole-Person Wellness Model?
In 1961, a physician named Halbert L. Dunn first introduced the term wellness. Dr. Dunn described it as a lifestyle approach for pursuing physical and psychological well-being. The concept of wellness was expanded by Bill Hettler, co-founder and president of the board of directors of the National Wellness Institute. Dr. Hettler proposed interdependent, whole-person wellness for the six-dimension wellness model: physical wellness, emotional wellness, spiritual wellness, intellectual wellness, occupational wellness and social wellness (See Figure 1). The working definition of each dimension is as follows:
Physical Dimension of Wellness
This recognizes the need for regular physical activity. Physical development encourages learning about diet and nutrition, while discouraging the use of tobacco, drugs, and excessive alcohol consumption. Good physical wellness is met through the combination of good exercise and eating habits.
Emotional Dimension of Wellness
This recognizes the awareness and acceptance of your feelings. The ability to form relationships with others based on mutual commitment, trust, and respect is a critical part of emotional wellness.
Spiritual Dimension of Wellness
This recognizes your search for meaning and purpose in life. An example is peaceful harmony between internal personal feelings and emotions through life and measuring those against personal values.
Intellectual Dimension of Wellness
This recognizes your creative, stimulating mental activities. A well-rounded person expands their knowledge and skills while discovering the potential for sharing their gifts with others.
Occupational Dimension of Wellness
This recognizes personal satisfaction in your life through work. Individuals can convey their values through involvement in activities that satisfy them.
Social Dimension of Wellness
Encourages contributing to your environment and community. The social dimension emphasizes the interdependence between others and nature.
Figure 1. A Whole-Person Wellness Model.
Why is Wellness Important?
The number of older adults over the age of 65 is increasing, and many of them live alone without support from a caregiver. As a result, then need to be more physically, emotionally, spiritually, intellectually, occupationally and socially healthy for independent living. The benefits of improved whole-person wellness for older adults are the following:
- Increased quality of life.
- Longer and healthier life.
- Active social interaction.
- Mental and emotional health.
- Active part of the workforce.
- Financial independence.
How to Improve Wellness Participation
The most important element of improving older adults’ health is to promote their participation in wellness activities. Through community support, needs awareness and education, older adults are expected to achieve the goal of increasing their participation in wellness programs.
Community Support
In a survey of Oklahoma community centers, findings showed that the centers provide one or more wellness activities for older adults. Findings from the survey indicated that 16 percent of the centers offered activities for all six dimensions. In terms of the six dimensions, the following activities were addressed, in decreasing order: physical, social, spiritual, intellectual, occupational, and emotional needs.
Activities for the physical dimension were offered by 85 percent of the centers. These activities were the most diverse, consisting of a variety of individual and group exercises focused on muscle strength and endurance, flexibility, coordination, and balance. All activities were held in the same physical space. The most frequent activity was the use of exercise equipment such as treadmills. Other exercise included walking, dancing, video exercise, aerobics, and bicycling. Additionally, planned meals and health education were frequent activities related to the physical dimension.
Activities for the social dimension were offered by 87 percent of the centers. Respondents indicated that games, such as bingo, dominos, cards, and puzzles, and parties/gatherings for family and friends were the frequent social activities aimed at creating and maintaining healthy relationships. Spiritual activities were offered in 61 percent of the community centers. These activities, which were more personal than others, included prayers for meals and bible reading. For the intellectual dimension, 55 percent of community centers offered activities. The most frequent activity noted was the participation in educational programs such as computers, word seek, story telling, autobiographies, travel, library, and training. Activities that contribute to the occupational and emotional dimensions were identified as less frequently offered by community centers. Occupational activities were offered in 37 percent of the centers, while activities for the emotional dimension were offered in 31 percent of the centers. The comprehensive whole person wellness model, which includes physical, emotional, spiritual, intellectual, occupational, and social dimensions, needs to be addressed further in rural community centers for older adults.
Needs Awareness
A senior center wellness program survey identified that older adults are especially concerned about good nutrition, health issues (cholesterol, blood pressure, heart disease, arthritis, hearing, osteoporosis, and diabetes), promoting restful sleep, tips for slowing the aging process, coping with change, forming a living will, exercise, coping with the loss of a spouse, and dieting. Community centers could incorporate these topics in their wellness programs and as a result, increase older adults’ awareness of wellness programs.
Education
Older adults often require support with their wellness needs. Nutritional intake, medicine and medical issues, and proper exercise are some of the topics for which older adults require an expert’s knowledge. Communities could focus on educating older adults about how to increase control over and improve their health in areas where special information is required.
How to Practice Wellness Activities in Daily Life
People often fail to realize that enhancing wellness can be achieved by everyday activities. The following are some of the examples of wellness activities that older adults can practice in their daily life. It is recommended that older adults make these wellness activities part of their daily routine:
- Eating: Good eating habits can be the first step for being healthy. Physical changes such as digestive problems due to aging, emotional changes such as loneliness, and social changes such as income, may influence older adults’ nutritional intake. According to the USDA MyPyramid food groups, 6 oz. of grains, 2.5 cups of vegetables, 2 cups of fruit, 3 cups of milk, 5.5 oz of meat and beans, and 6 teaspoons of oil are recommended for a daily 2,000 calorie diet. Additionally, regular meal times, smaller meal portions (five to six meals per day), daily activity, attractive food presentation, and occasional eating out can help older adults maintain healthy eating habits.
- Bathing: Bathing can be an effective wellness experience that promotes physical well-being through movement and hygiene, emotional well-being through taking care of yourself and practicing daily routine activities, and spiritual well-being through relaxation.
- Walking: Walking is one of the easiest and safest physical activities. Simple physical activity like walking can reduce the rate of coronary heart disease by 5 percent to 25 percent. It is often recommended that older adults should regularly take a walk in parks or neighborhoods. Additionally, mall walking has been proven effective in maintaining good health. Mall walking gives the benefit of not only physical fitness but also emotional and social wellness. By walking around with other shoppers, older adults can have a feeling of belonging and social interactions with others.
- Talking: Talking to others is a great way of expressing feelings, controlling stress, interacting with others, creating and maintaining relationships, and sharing interests. It promotes emotional and social wellness for older adults.
- Reading: Reading is a good mental exercise for intellectual and emotional wellness. Older adults can experience happiness and joy of life, get new information, and be connected with other people through reading. Most community libraries are senior friendly and offer various wellness programs and resources as well.
References
Ardell, D. B. (2000). What is wellness? Retrieved on January 20, 2008.
Eaton, C. B., Lapane, K. L., Garber, C. E., Gans, K. M., Lasater, T. M., & Carleton, R. A. (1999). Effects of a community-based intervention on physical activity: The Pawtucket heart health program. American Journal of Public Health, 89(11). 1741.
Hermann, J. R. (2006). Food intakes in later years. Fact Sheet T-3148, Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service.
Kang, M., & Russ, R. (2008). Actives that promote wellness for older adults in rural communities. Environmental Design Research Association Conference, Veracruz, Mexico.
Moller, J., ASID, Renegar, C. (2003, October). Bathing as a wellness experience. Nursing Homes Magazine, 108-111.
Shellman, J. (2000). Promoting elder wellness through a community-based blood pressure clinic. Public Health Nursing, 17(4), 257-263.
Stephenson, L. E., Culos-Reed, S. N., Doyle-Baker, P. K., Devonish, J. A., & Dickinson, J. A. (2007). Walking for wellness: Results from a mall walking program for elderly. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 29(3/4), S234.
The six dimensional wellness model (n.d). Retrieved January 18, 2008, from National Wellness.
United States Department of Agriculture. MyPyramid: Steps to a healthier you. Retrieved
January 27, 2008.
Mihyun Kang, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor
Randall Russ, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Jay Sang Ryu
Ph.D. Student