Identification of Grasses Commonly Found in Oklahoma Wheat Fields
Cheat
(Bromus secalinus)
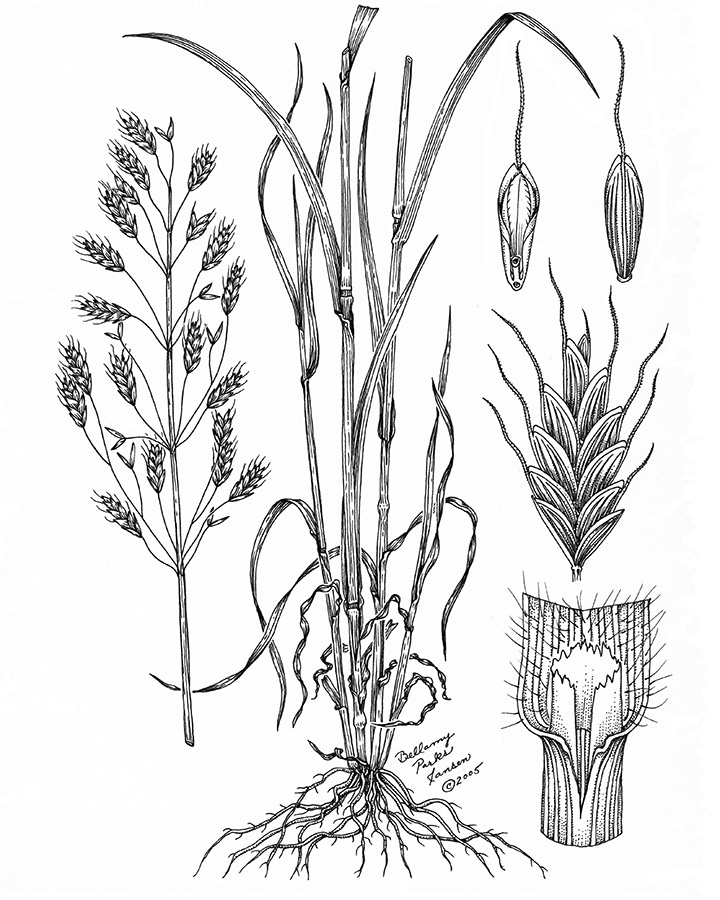
Cheat
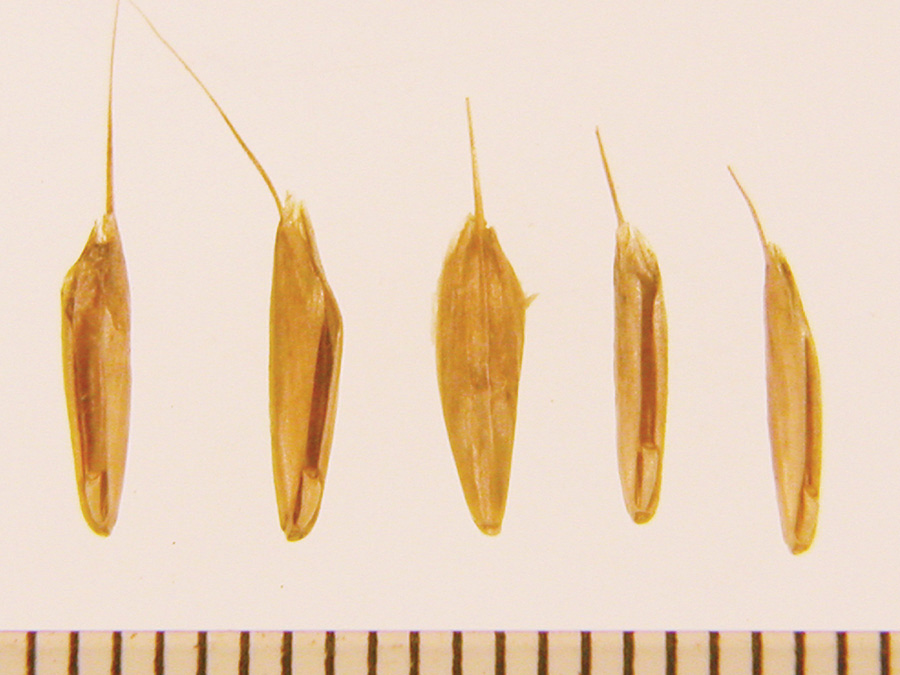

Canoe-shaped florets with arched rachilla joint. Short awn on most florets.
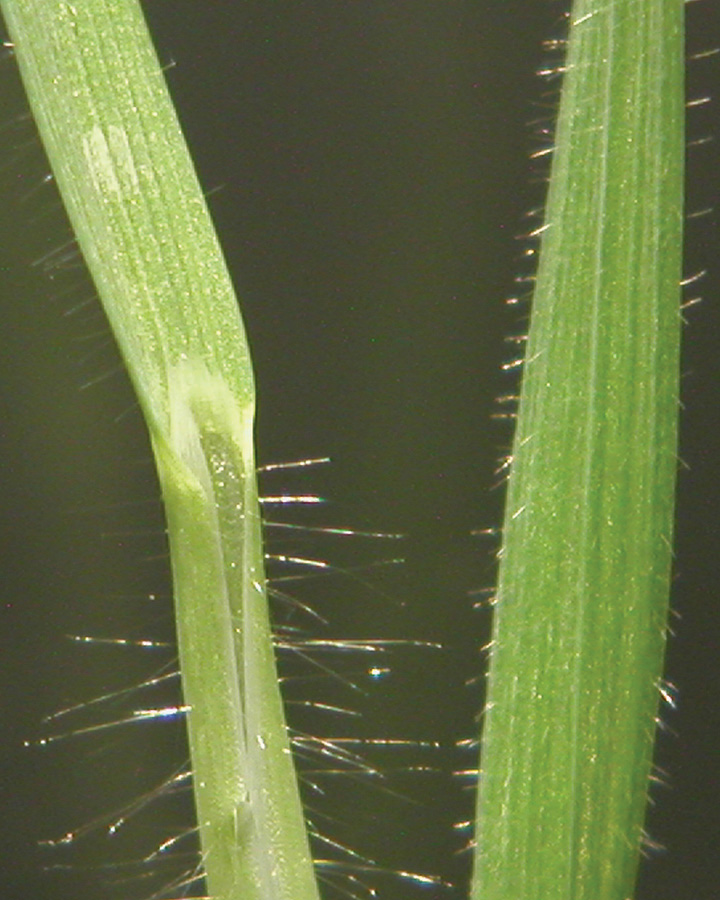

Dense pubescence covers seedlings. Use attached floret for ID.
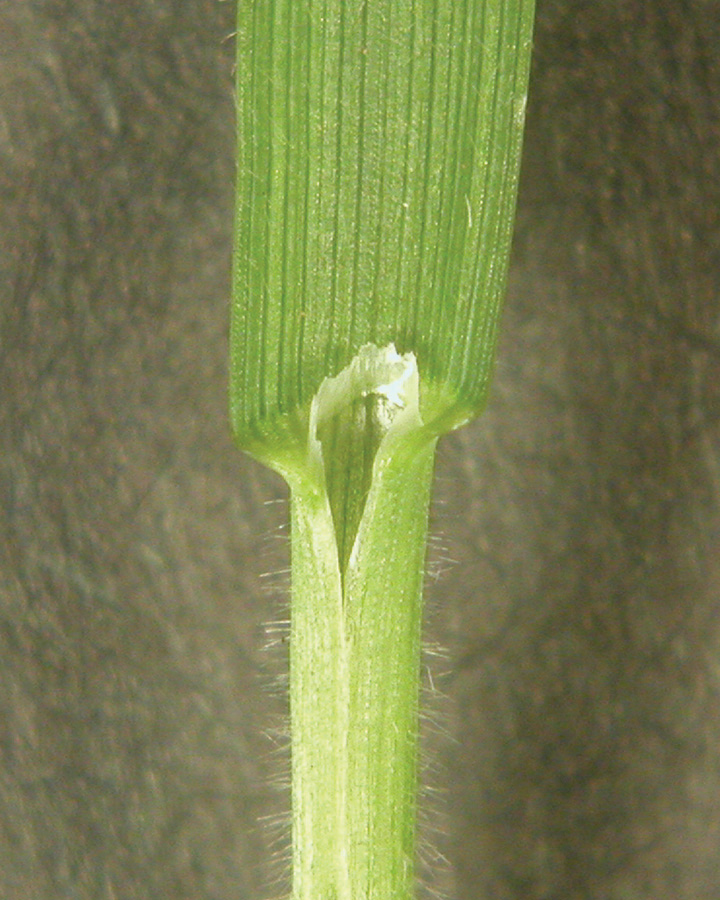

Hairs present on blade and sheath until near maturity, then hairs found only on blade
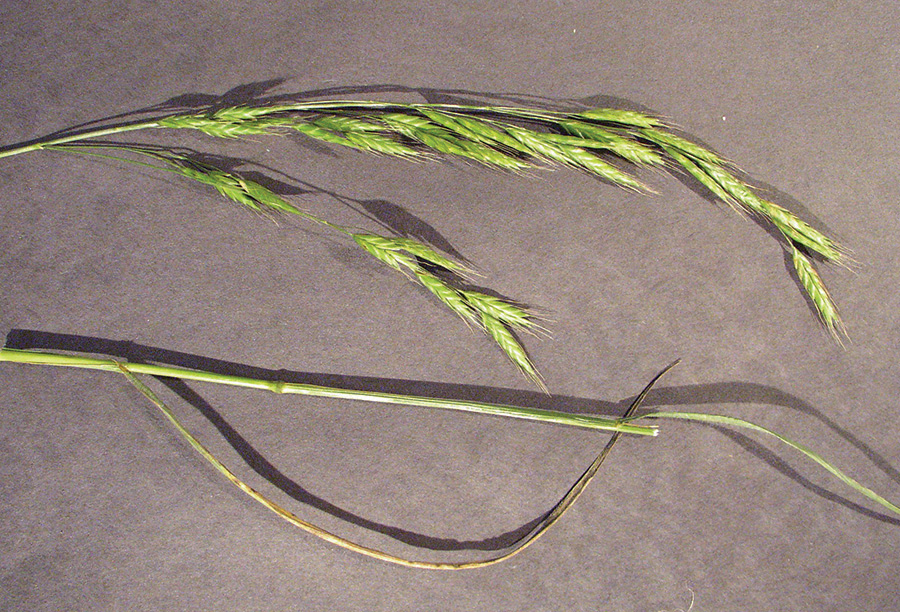

Open panicles; blades pubescent.
Downy & Japanese brome
(Bromus tectorum & B. japonicus)
Downy brome
Japanese brome
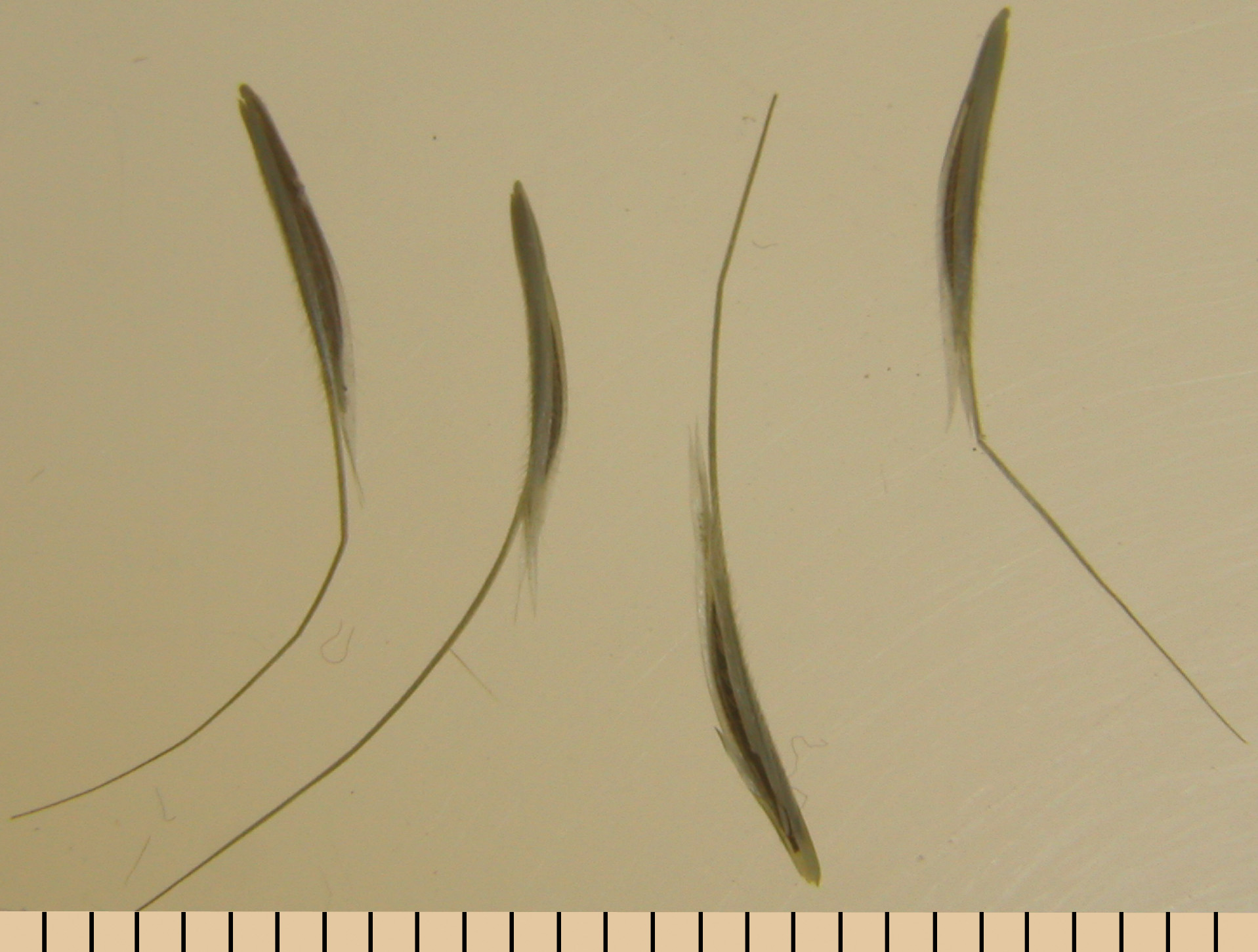


Downy brome floret arched with long awn and numerous hairs across back. Japanese brome floret is similar to cheat.

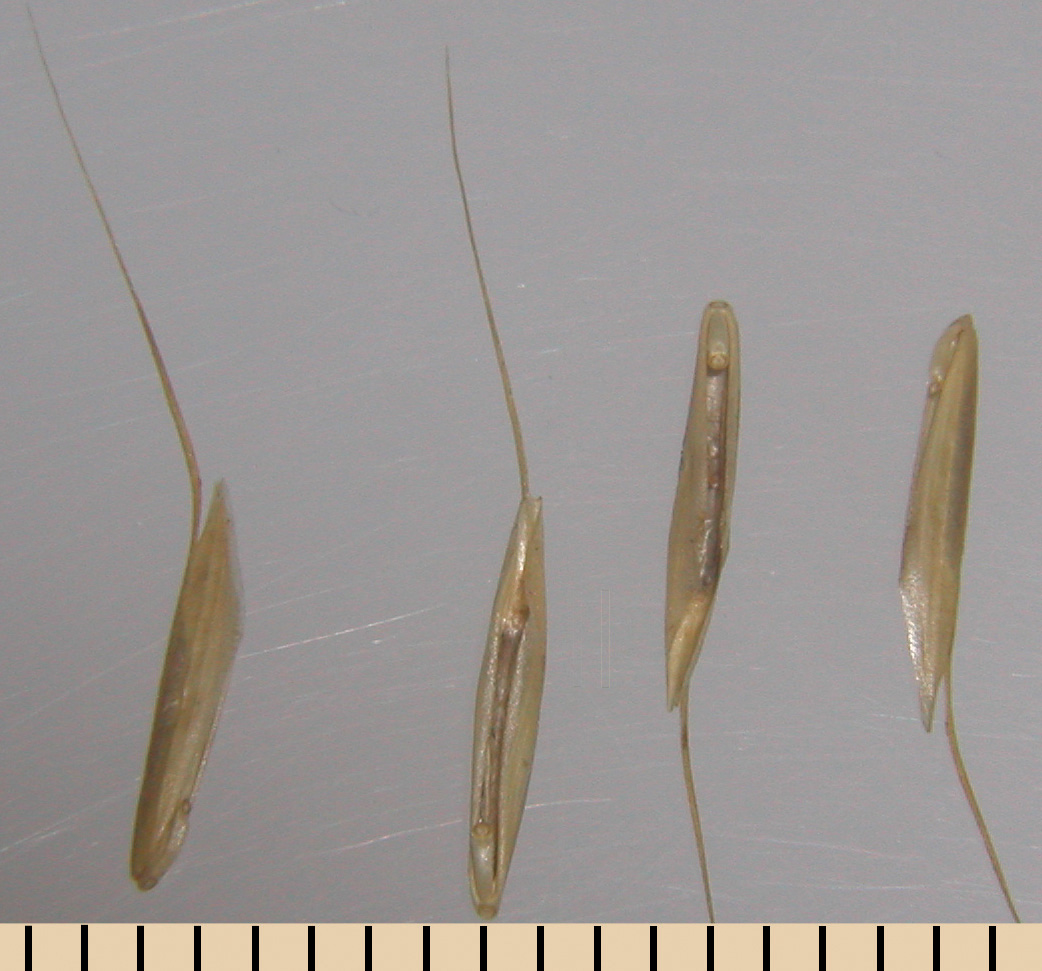
Dense pubescence covers seedlings. Use attached fl oret for ID.

Dense hairs found on blade and sheath at maturity.


Downy brome (left) and Japanese brome (right):
open, somewhat nodding panicles; dense pubescence on stems and leaves giving the plant a grey-green color.
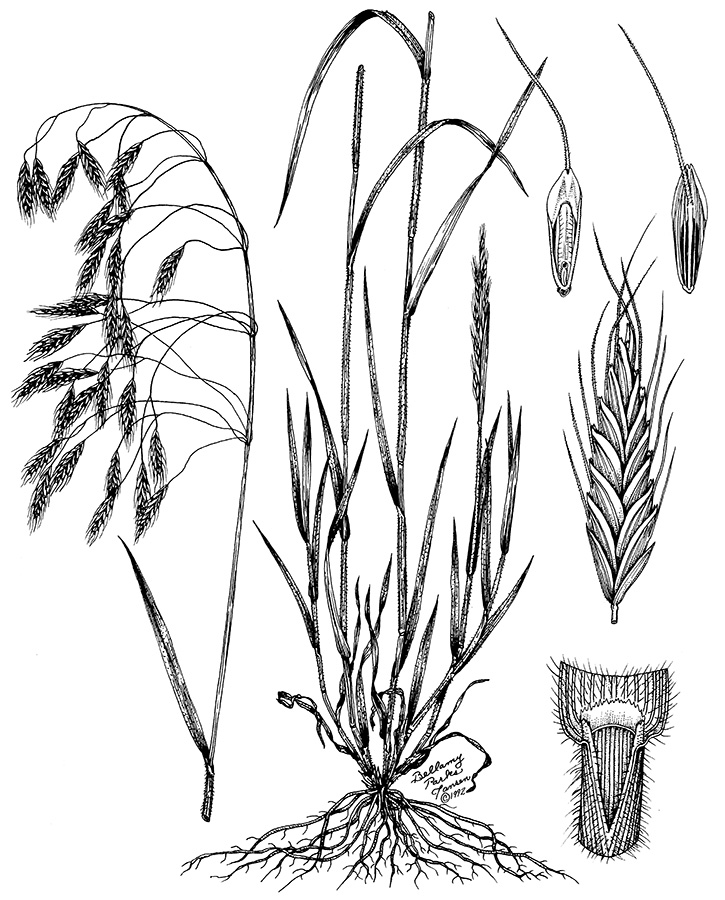
Rescuegrass
(Brumus catharticus)
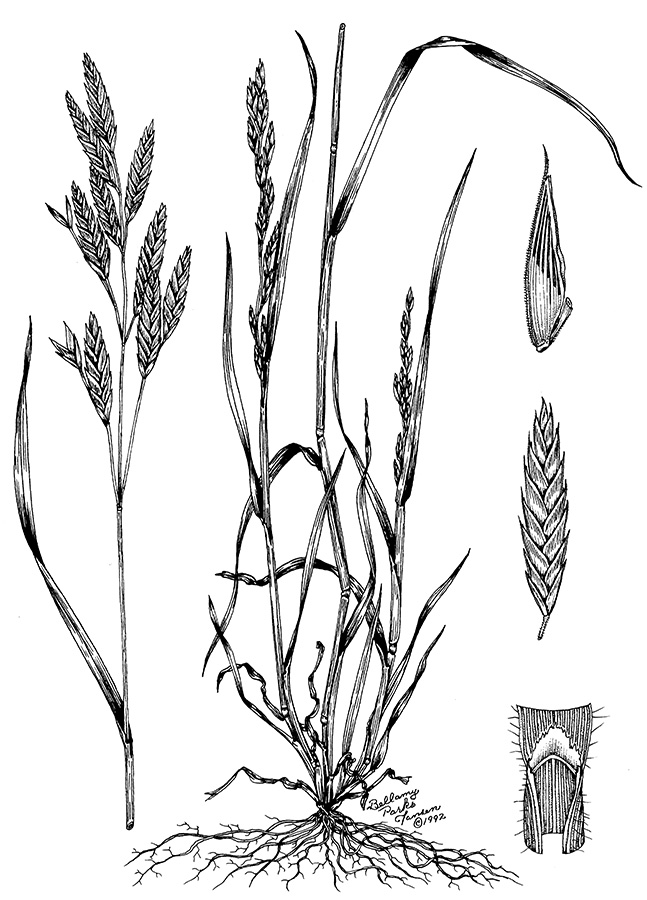
Rescuegrass

Flat florets with distinct angles.

Dense pubescence covers seedlings. Use attached floret for ID.

Scattered hairs found on blade and sheath.

Open panicles with strongly flattened spikelets and tightly overlapping florets; little or no pubescence on stems and upper leaves.
Feral rye
(Secale cereale)
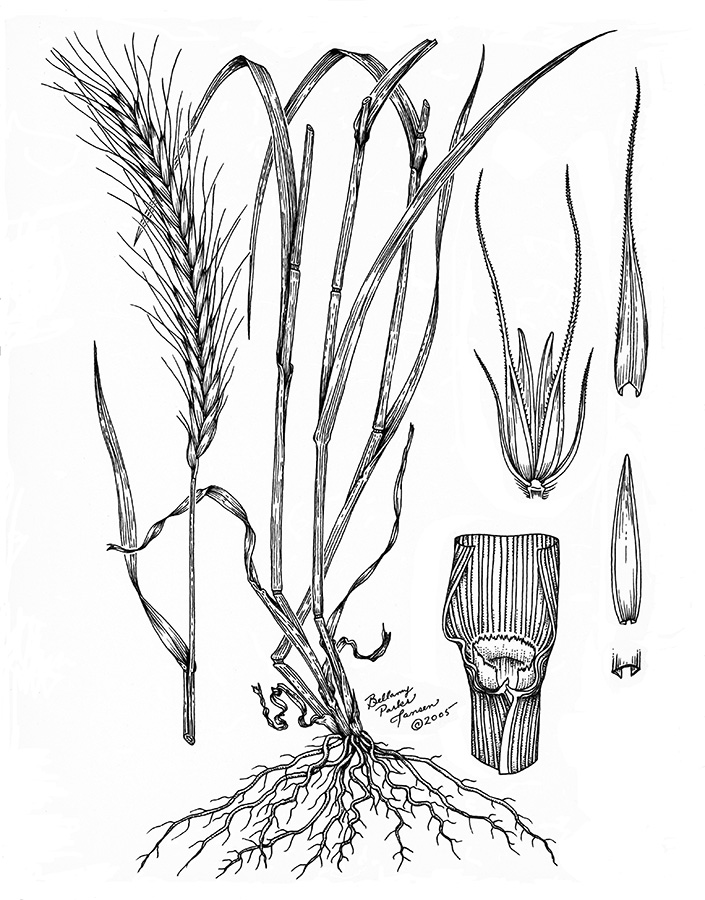
Feral rye
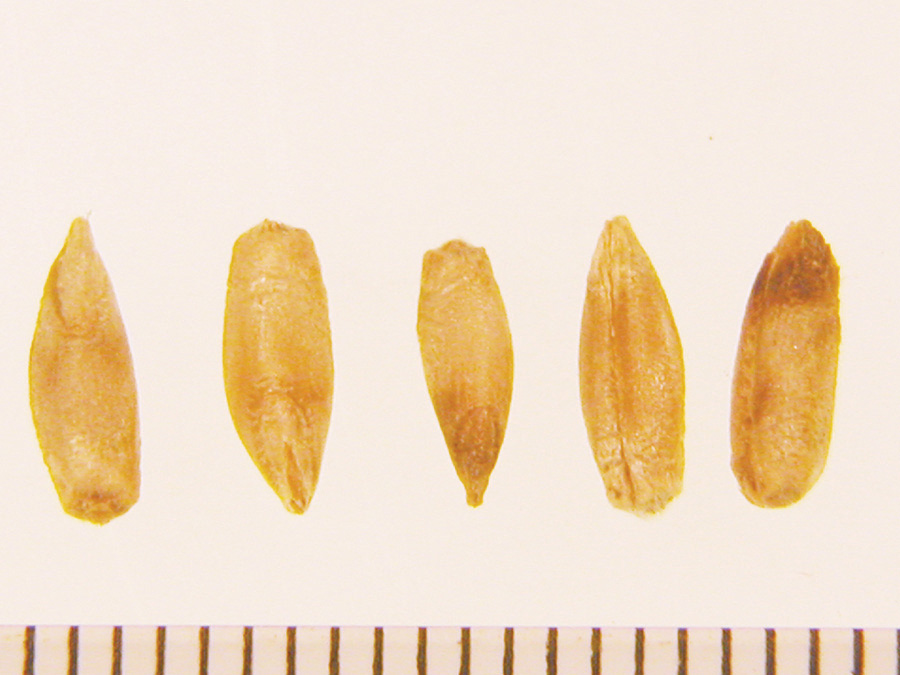

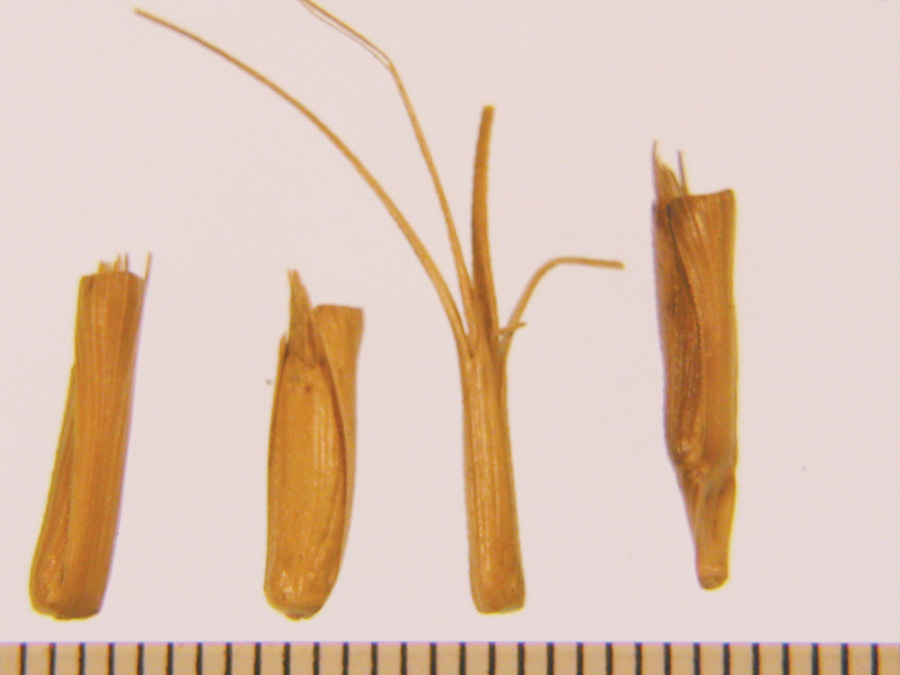
Caryopsis tan, brown, grey, or black. Germ end of caryopses usually pointed.

Seedlings may be covered pubescent or glabrous. Use attached caryopsis for ID.

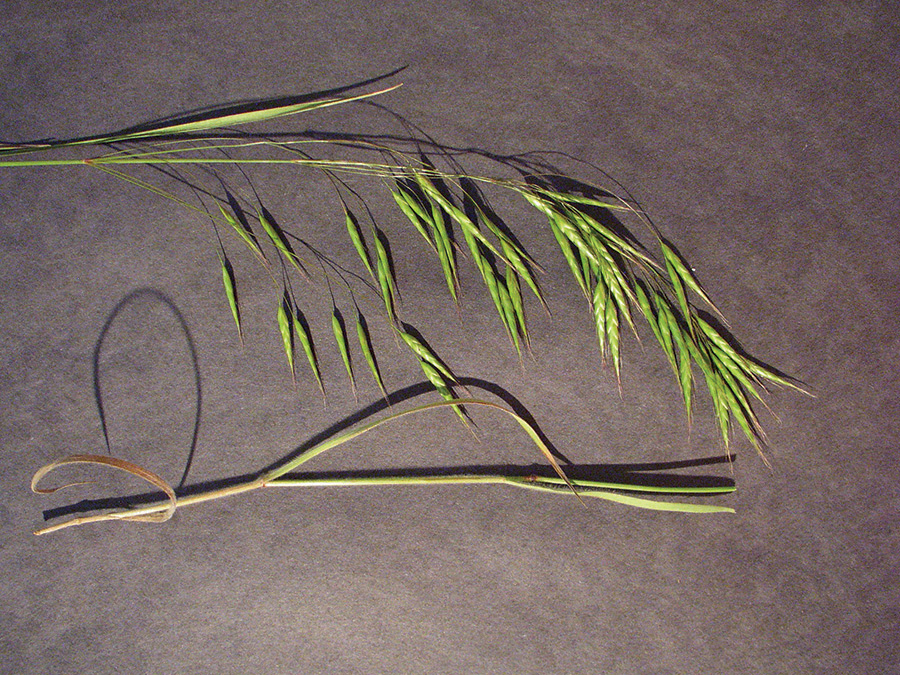
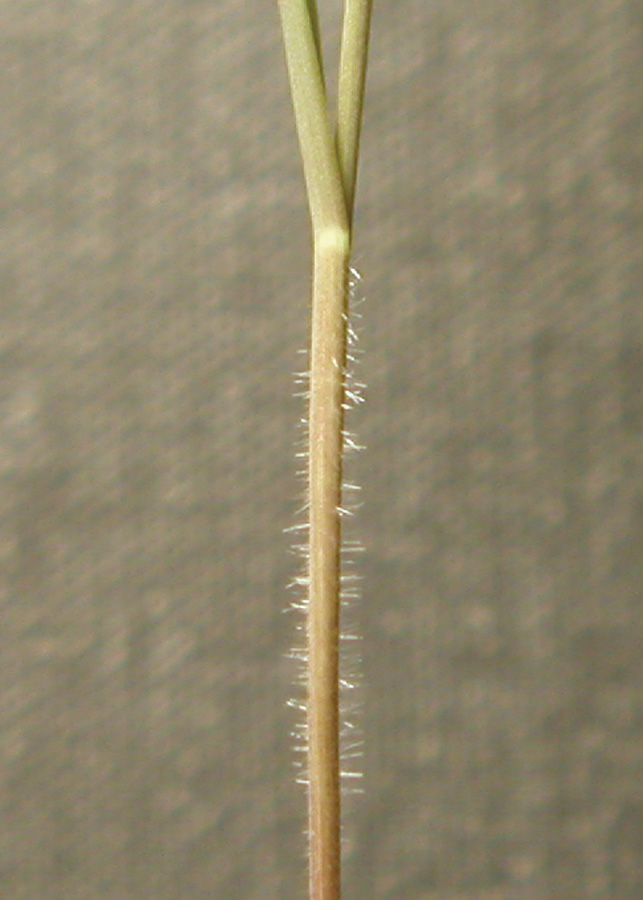
Stems and leaves may be pubescent or glabrous. Typically grows more robust than wheat. May have small auricles.
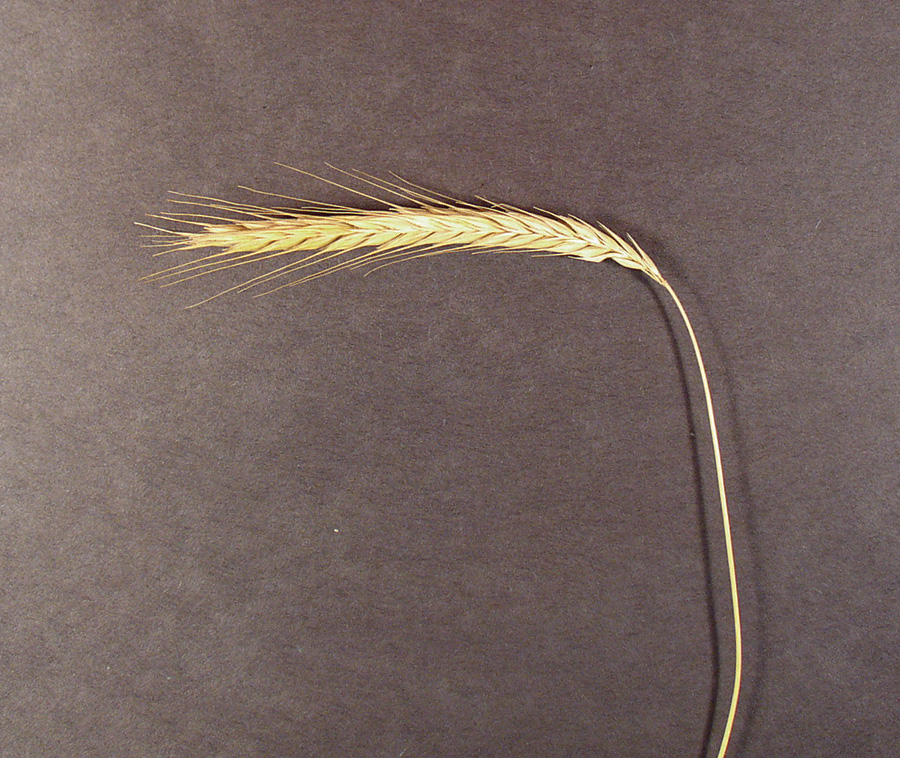

Elongated, arching spikes generally rising 8 to 12 inches above those of wheat.
Jointed goatgrass
(Aegilops cylindrica)
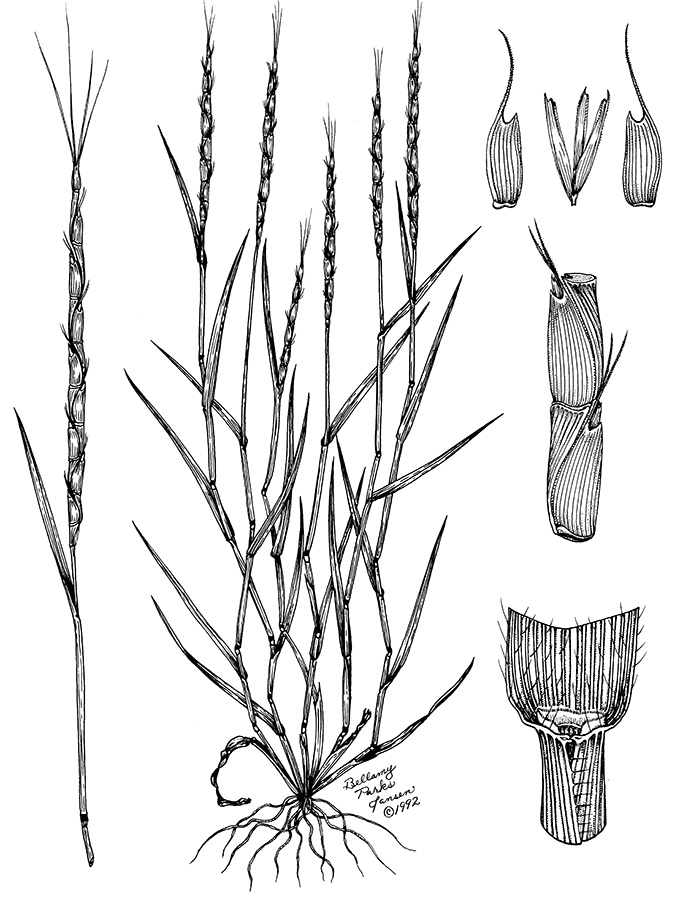
Jointed goatgrass

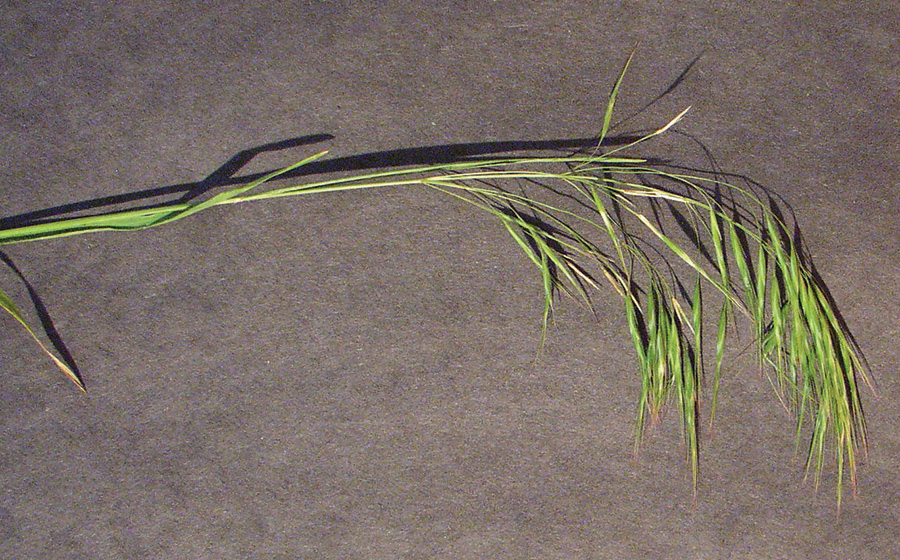
Each joint may produce 1 to 3 seedlings. Upper joints often shattered before harvest and lower 1 to 3 joints remain in straw after harvest.
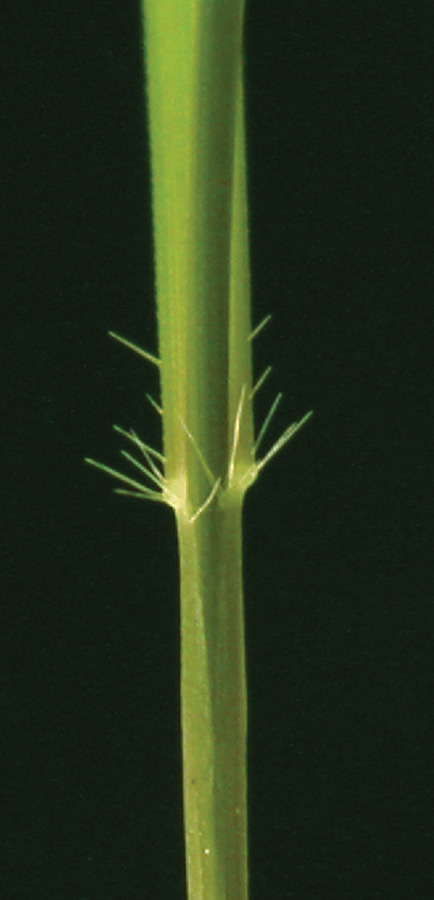

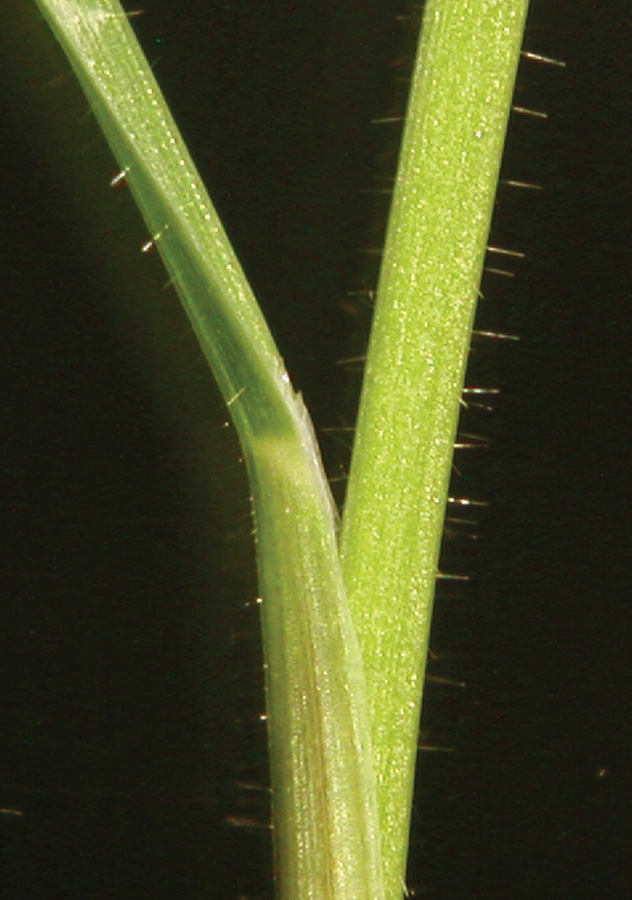
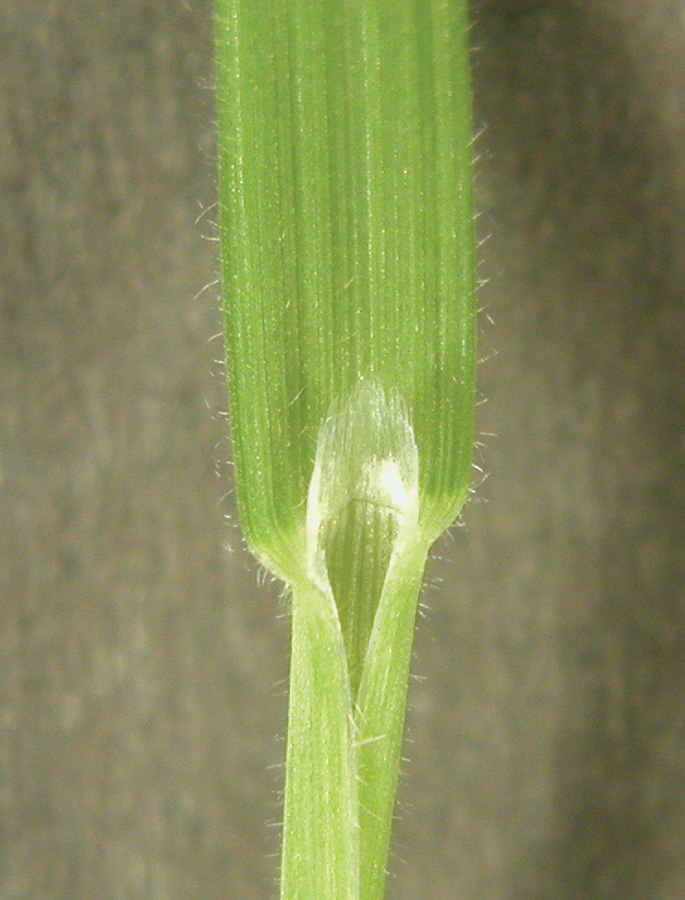
Long hairs obvious on margin near collar. Use attached spikelet for ID.
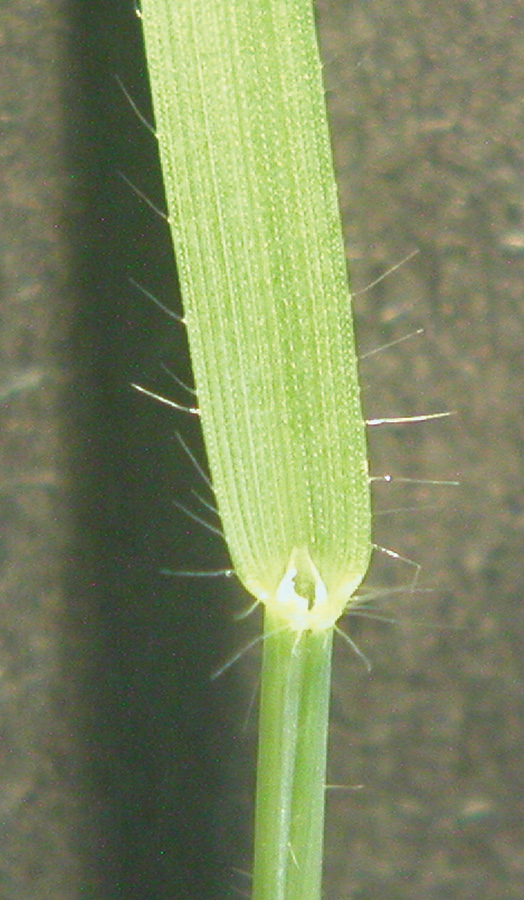

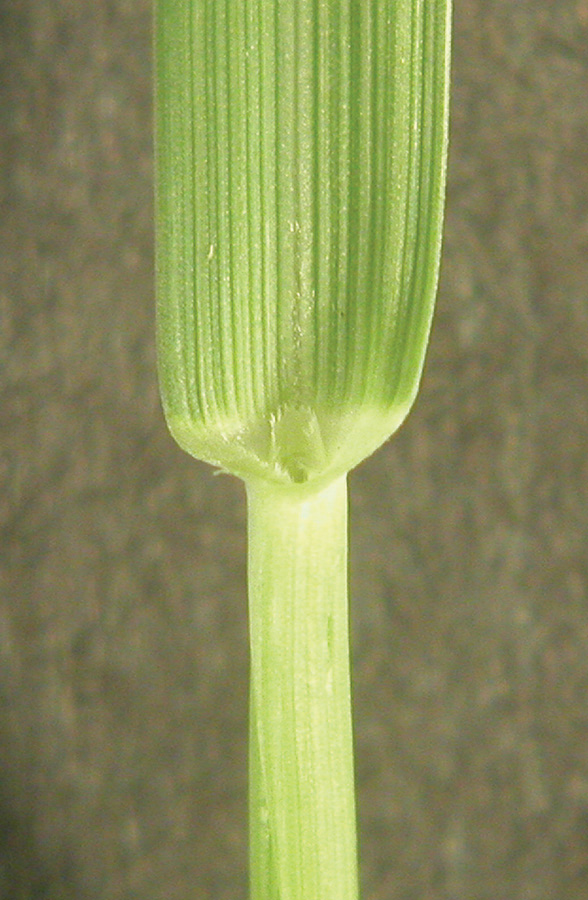
Long distinct hairs present on margins near collar. Small auricles.

Clindrical spikes with 2 to 12 joints and awned florest.
Italian ryegrass
(Lolium multiflorum)
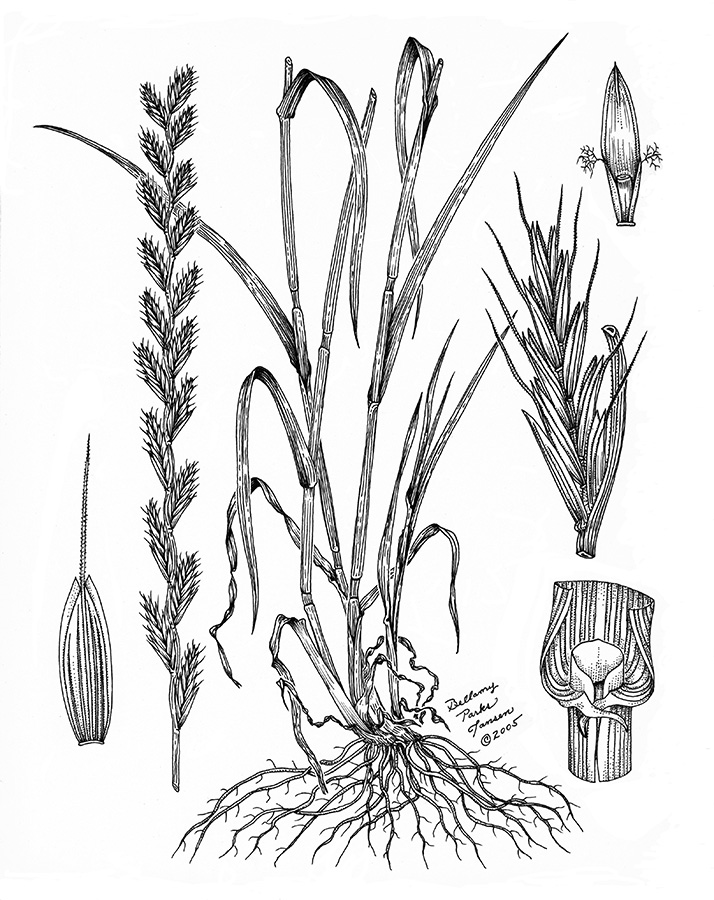
Italian ryegrass
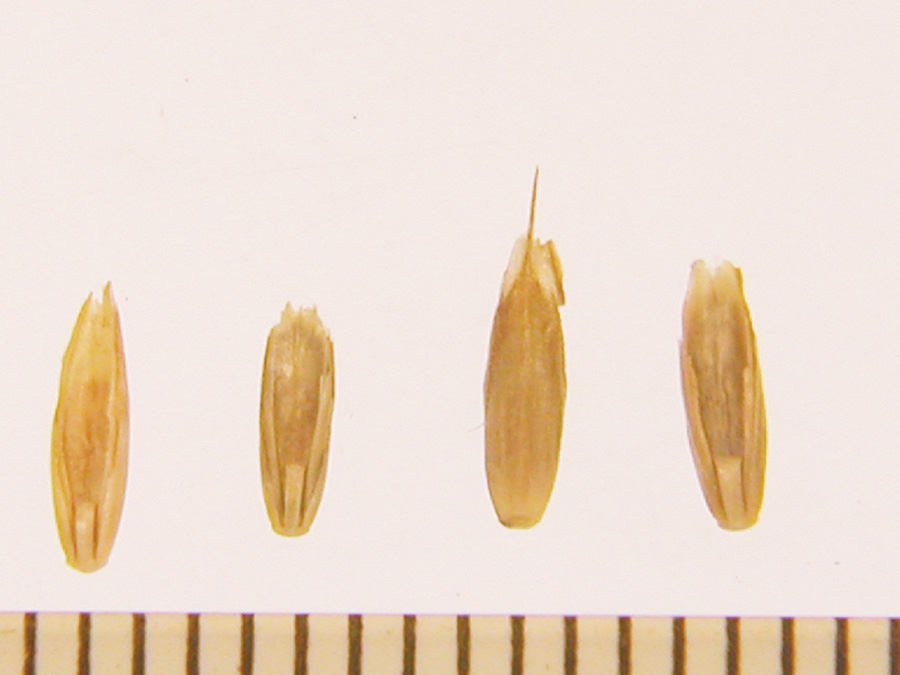

Elliptic florets with straight rachilla joint and short awn. Commonly sold to overseed lawns and pastures in the fall and winter months.
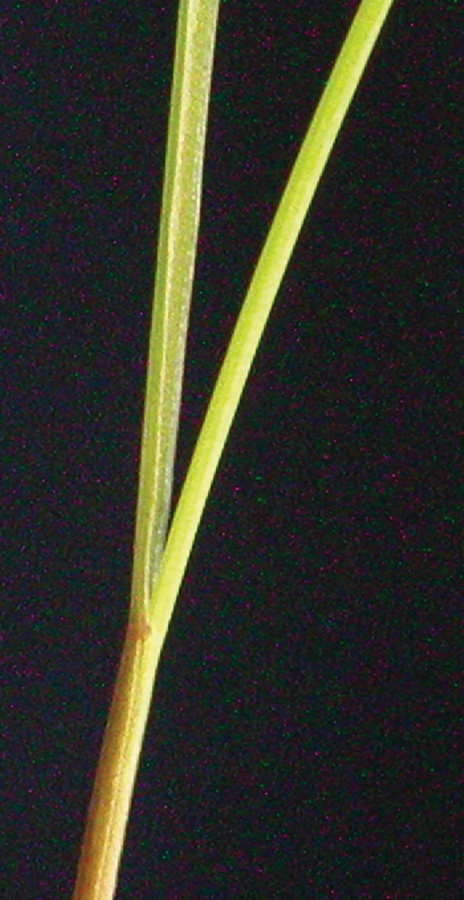

Leaves glabrous, often shiny or waxy. Use attached floret for ID.
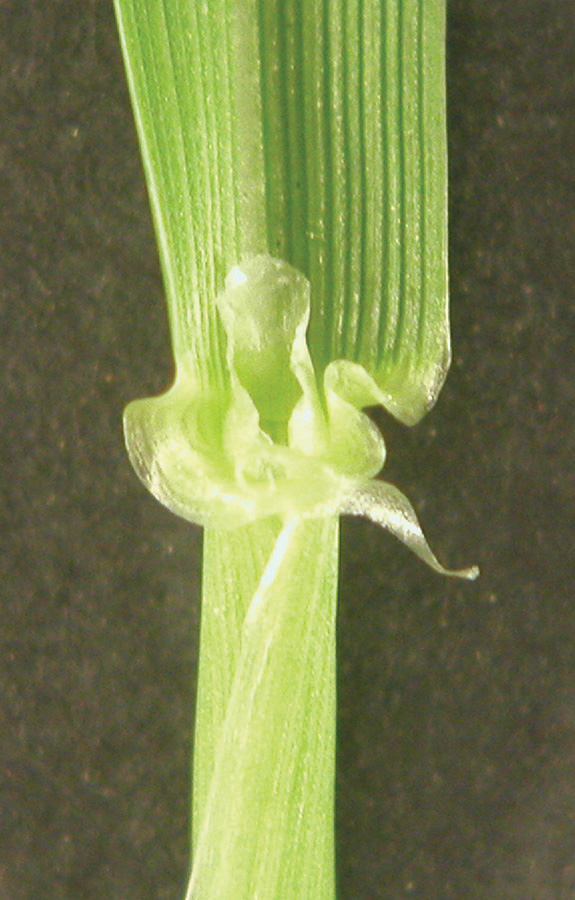

Leaves glabrous, often shiny or waxy; auricles clasp stem.

Elongated spike with 5 to 38 spikelets. Each spikelet comprises 4 to 17 florets.
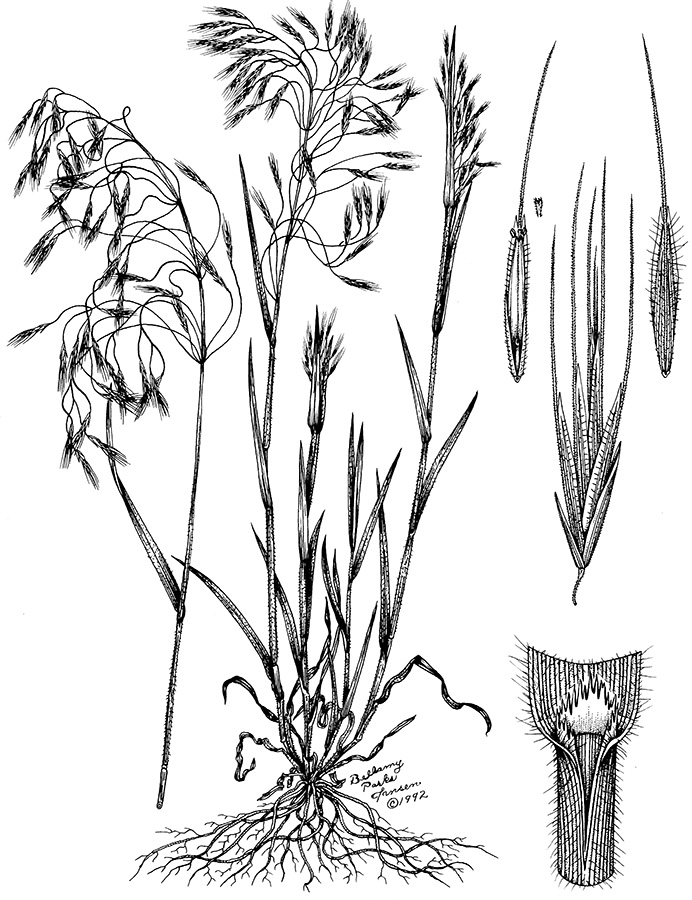
Wild oats
(Avena spp.)
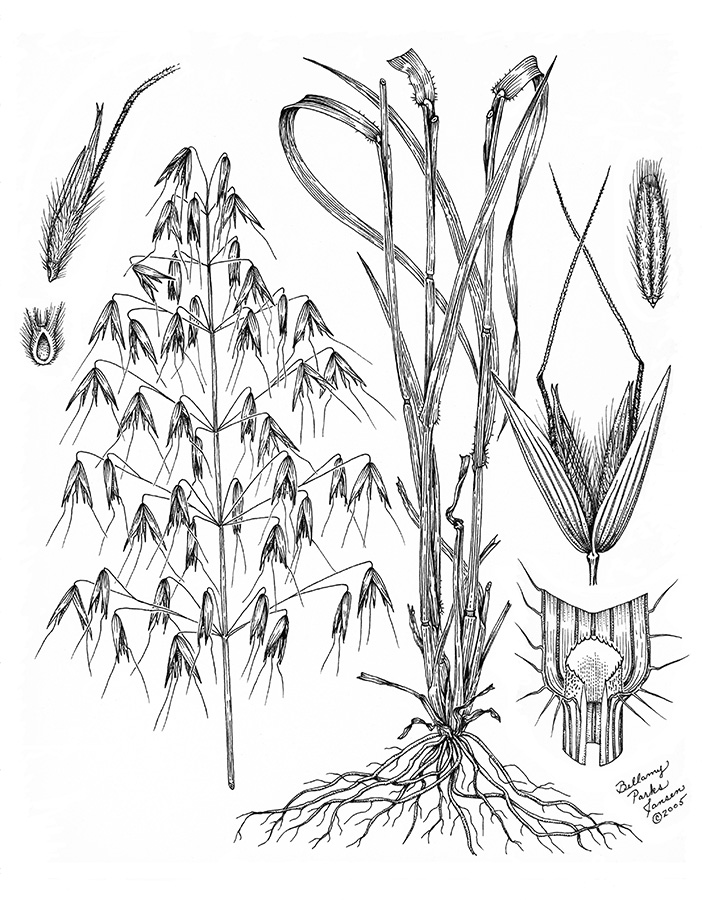
Wild oats

Florets with sucker-mouth scar at basal end and twisted awn from back. At least 3 species present; florets exhibit considerable variation in color and pubescence.
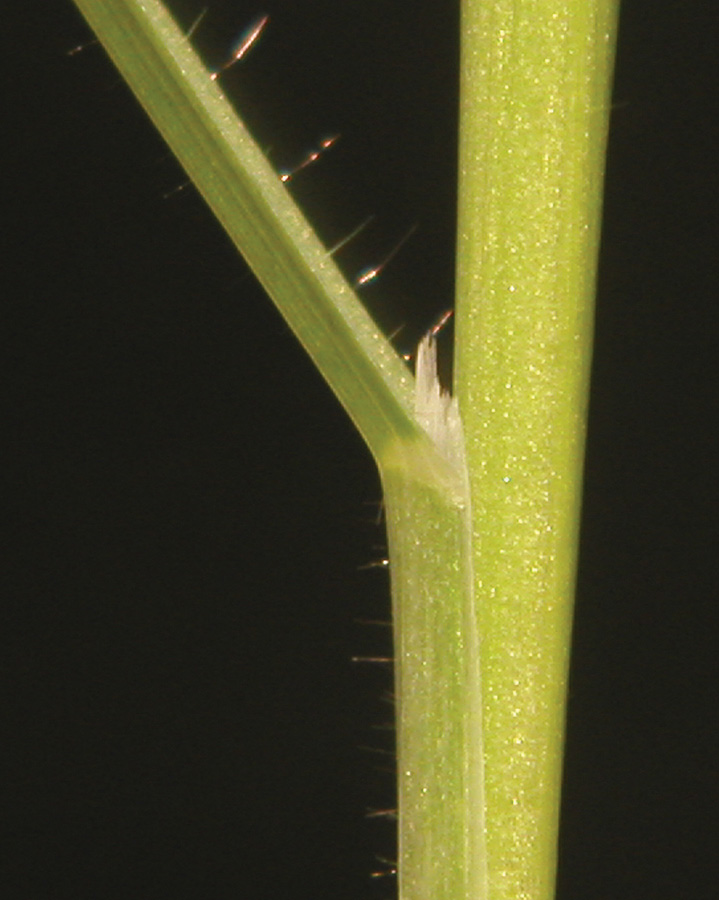

Scattered hairs on seedlings, color often appears blue. Leaves twist opposite of wheat. Use attached floret for ID.
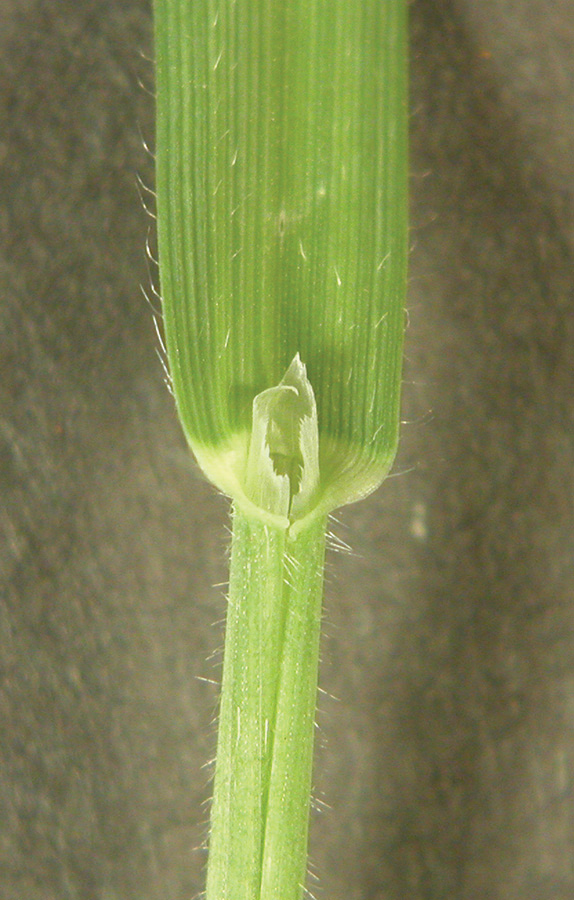

Scattered hairs on leaves and stems. Very long ligule. Leaves twist the opposite direction of wheat.
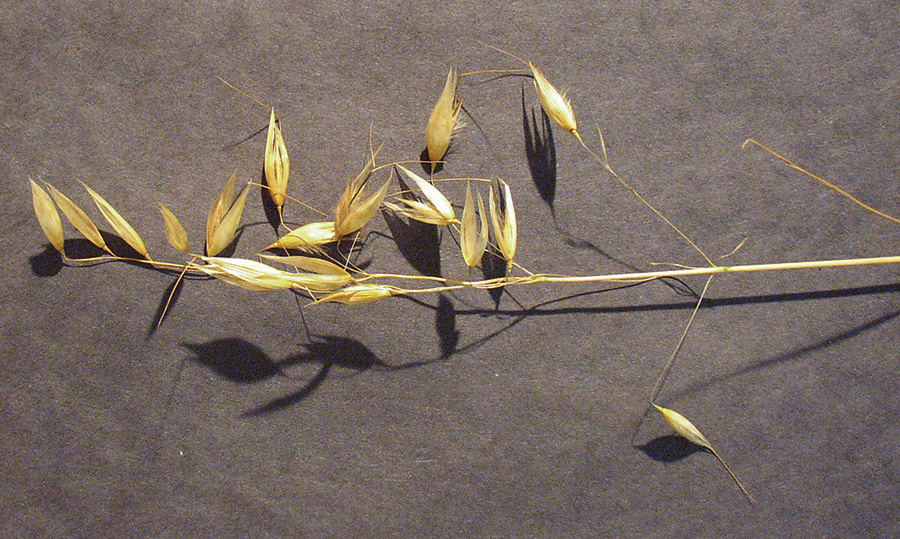

Open panicles with drooping spikelets on abruptly bent pedicels; 2 to 4 florets per spikelet.
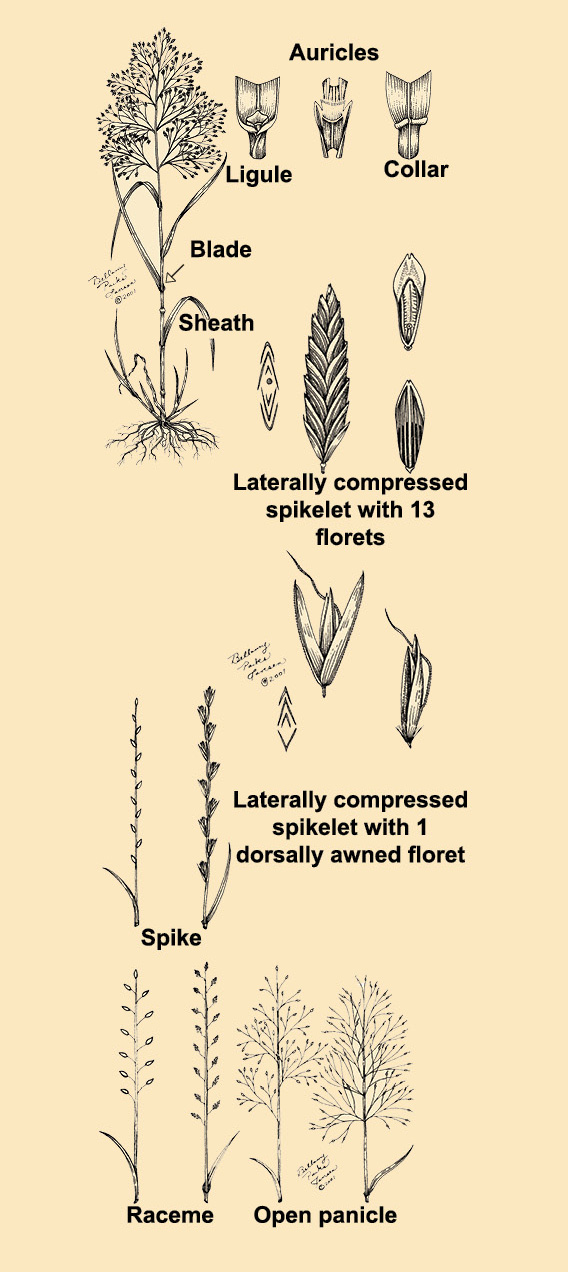
- Auricles – pair of ear-like lobes or appendages at base of blade or apex of sheath
- Awn – bristle-like appendage extending from apex or back of floret
- Blade – thin expanded portion of the leaf
- Caryopsis – dry, indehiscent, 1- seeded fruit with seed coat fused to pericarp; synonym is grain
- Collar – region on outside of leaf at junction of blade and sheath
- Floret – flower and two associated bracts, the lemma and palea
- Glabrous – devoid of hairs
- Inflorescence – arrangement of spikelets and associated structures on an axis
- Leaf margin – edge or border of the leaf
- Ligule – membranous appendage on inner surface of leaf at junction of leaf sheath and blade
- Panicle – branched inflorescence comprising rachis, one to several series of branches, and pedicels bearing spikelets
- Pedicel – stalk bearing a spikelet; ultimate axis of panicle or raceme
- Pubescence – collective term for hairs that are present on a plant organ
- Raceme – branched inflorescence consisting of central axis bearing multiple pedicels terminating in spikelets
- Rachilla – axis of spikelet
- Sheath – long, tubular, basal portion of the leaf that encircles the stem Spike – unbranched inflorescence consisting of central rachis bearing one or more sessile spikelets
- Spikelet – highly modified inflorescence typically consisting of two glumes, one or more florets, and rachilla
Case Medlin
State Weed Specialist
Ronald J. Tyrl
Plant Taxonomist
Sponsored by:
Oklahoma Cooperative extension Service
Oklahoma Wheat Commission
National Jointed Goetgress Research Program