Fall Gardening
Gardening is a year-round activity. Those who garden develop an appreciation and a desire for fresh, nutritious vegetables and fruits. In many situations, the best way to obtain fresh vegetables is to grow them at home.
Some of the best quality garden vegetables in Oklahoma are produced and harvested during the fall season when warm, sunny days are followed by cool, humid nights. Under these climatic conditions, plant soil metabolism is low; therefore, more of the food manufactured by the plant becomes a high-quality vegetable product.
Successful fall gardening begins much earlier than the fall season. Factors to be considered are adequate soil preparation, available garden space, crops to be grown, space for each crop, varieties to use, and obtaining the quantity and varieties of seed.
Some crops are more easily grown when seeds are planted early, and then the seedlings are transplanted to the garden at a later time. Growing seedling plants under partial shade and with insect protection may be more easily accomplished than seeding directly in the garden.
Usually, the time of planting is dependent upon the length of time required to produce the crop. Some crops may be limited to a specific planting date. Others, such as radish, may produce a crop in 20 to 30 days, thus allowing the gardener to make successive plantings for a more continuous supply.
Cold frames and row covers make year-round home food growing possible in Oklahoma. Salad crops are particularly successful if grown in cold frames and harvested on an as-needed basis in January and February.
Since seeds and transplants may be planted in the garden during June, July, August, and September, supplemental water is a necessity to aid seed germination and plant growth. Many gardeners may have a limited supply of water available, and furrow or drip irrigation applied only in the row might provide for suitable early growth. Fall rains may wet the dry soil between the rows. Vegetables grown in the fall not only provide fresh produce for the season, but also provide quantities that can be harvested and stored for use in the months following fall frosts and freezes.
Soil Preparation
The ease with which one is able to grow plants is greatly influenced by characteristics of the soil. Modifying or improving the soil prior to and during the gardening season is important.
Various fertilizer elements are necessary for plant growth and many can be easily applied. However, other aspects of soil improvement may not be as easily and readily accomplished. In a very sandy soil, the incorporation of organic matter would reduce rapid drying of the soil and improve nutrient availability. In a very heavy clay soil, organic matter would improve soil aeration, water absorption, and drainage.
Desirable Garden Soil
Soil should absorb water readily, not form a crust upon drying, and drain sufficiently so that it does not become waterlogged. A porous soil contains more air, which is necessary for vigorous root growth. As organic matter decomposes, soil texture improves and nutrient availability should increase. More information on garden soil improvement is given in fact sheet HLA-6007, “Improving Garden Soil Fertility.”
The soil must contain a supply of water and available fertilizer nutrients. Soils that produced a spring vegetable crop will be more easily managed than those with established grasses and weeds.
Additional fertilizers may be beneficial to stimulate growth and production. These might be incorporated in the soil prior to planting or applied on the soil surface later.
Planting Seeds and Obtaining a Stand of Plants
Climatic conditions of July and August involve high soil temperature, high light intensity, and rapid drying of the soil, resulting in an increase in the problems of obtaining a uniform stand of plants. Achieving a full stand of plants in the heat of summer may require special treatments. This might include shade over rows when seeded and supplemental watering to reduce soil temperature and aid in seed germination.
Viable seed, in order to germinate or sprout, must have the proper temperature, adequate moisture, and sufficient oxygen. The surface of the soil, when exposed to the summer sun, may become very hot (140°F or 60°C). Vegetable seeds should be planted no deeper than three times the diameter of the seed. With small seed such as carrot, this would be no more than 1/4 inch deep. At this depth and exposed in the hot soil, death of the seed due to high temperature would probably occur. It is also likely that such a soil, even when watered, might dry out quickly because of the high temperature. Unless the soil remains moist at the depth where the seeds have been planted, germination will not take place.
In order to achieve proper temperature and adequate moisture, apply mulch over the row following planting and watering or use materials such as screen wire strips, shade cloth, or boards to cover the row. This will moderate both soil temperature and soil moisture. (Figure 1d and 1e). Remove covers after seedling emerges.
Another desirable practice is to open the soil for the row somewhat deeper than in spring planting (Figure 1a). The seeds are planted in this furrow, covered, and watered (Figure 1b and 1c). In this manner, only the narrow trench would be watered, thus conserving a limited water supply. Later, one may cultivate along the sides of the row and fill soil to the same level of the remainder of the garden. In so doing, one may cover small grass and broadleaf weed plants that might be growing in the row (Figure 1f and 1g).
Some vegetables are most easily grown by planting seeds in a small seed flat, setting them in individual containers to grow for approximately one month, and then transplanting them to the garden. Those that respond most favorably to this method of handling include broccoli, cauliflower, Chinese cabbage, leaf lettuce, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage.
Prior to setting them in the garden, transplants may be conditioned or toughened by a reduction in the amount of water supplied and by exposure to full sunlight. This might require three to five days. Plant them in the garden in late afternoon to early evening to reduce transplanting shock. Water the plants as they are set. A water-soluble fertilizer may be used at this time, if necessary—following label directions.
To achieve maximum germination of lettuce seed, the planted and watered seed flat should be kept cool. This can be accomplished by placing the seed flat in a cool (60° to 70°F) location for four or five days, at which time seed may begin germinating. The seedlings should be transplanted to individual containers within a few days.
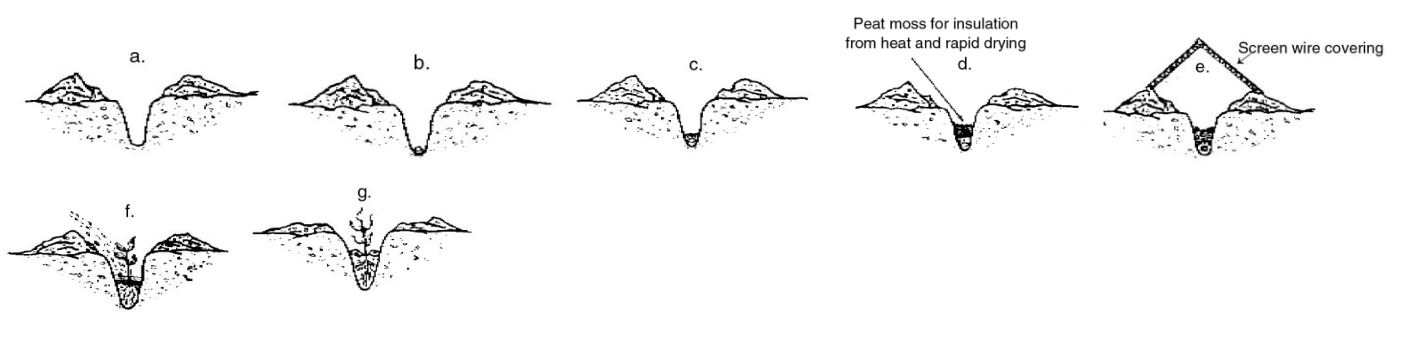
Figure 1. Method of planting fall vegetable seeds.
Vegetables for the Fall Garden
To some extent, the selection of crops will be influenced by what is presently in the garden and producing, family preference, space, water available for irrigation, and crops adapted for fall production. Some crops that were planted in the spring garden that may continue in production are tomato, okra, pepper, sweet potato, cowpea, and New Zealand spinach.
These plants may produce excellent yields in the later fall season if given proper care. If tomato, okra, or New Zealand spinach plants are too large for the space, prune them to reduce their size and also stimulate growth. If they are cultivated, it should be done very shallowly and used primarily to remove grass and broadleaved weeds. They should also be fertilized, watered, and mulched.
Fall Gardening Suggestions
- Seeds left over from planting the spring garden may be used in planting the fall garden if the seed is stored in a cool, dry location or in a refrigerator or freezer.
- Seeds that are stored in the freezer properly should remain viable for many years. Immediately following planting, return surplus seed to the freezer.
- In order to get early established growth, supplemental irrigation is desirable. Most vegetable crops will benefit from supplemental irrigation. Information on drip irrigation may be available from garden centers and county Extension centers. This technique allows an efficient method of irrigation.
- In order to conserve on water usage, water only the furrows or rows and wait for rainfall for general watering.
- Soak seeds overnight for planting (except beans and peas). This will hasten germination and seedling emergence when soil drying is most critical to plant growth.
- Cover seeded rows to reduce soil temperature and drying (Figure 1d and 1e).
Conditions that favor the germination of planted vegetable seed and luxuriant growth also favor the growth of grass and broadleaf weed plants. Mulch the soil or cultivate when the grass and broadleaf weed plants are very small and more easily destroyed (Figure 1f and 1g). This is a more critical problem than in spring gardens.
Insect pests may come into the fall garden and seriously damage plants within a week. Frequent checks and immediate protective measures must be used. In order for control to be effective, determine what kind or kinds of pests are causing damage. Use the proper kind of control material as recommended in fact sheet EPP-7313.
Table 1. Tender Vegetables – (harvest before frost).* Many varieties will do well. Select varieties that are early maturing and disease resistant.
| Kind | Time to plant | Method of Planting | Between Rows (inches) | In the Row (inches) | Depth to Cover Seed (inches) | Days From Planting to Harvest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beans, Bush | Aug 10-20 | Seed | 18-24 | 3-6 | 1.00 | 50-60 | |
| Beans, Cowpea | July 15-Aug 1 | Seed | 18-48 | 6-12 | 1.50 | 75 | |
| Beans, Pole | July 15-30 | Seed | 24-36 | 10-18 | 1.00 | 60-70 | |
| Beans, Lima | Aug 10-20 | Seed | 18-24 | 4-8 | 1.00 | 70-80 | |
| Cilantro | July 15-Aug 1 | Seed | 9 | 4 | 0.50 | When plant is 4-6 in. tall | |
| Corn, Sweet (3) | 15-Jul | Seed | 36 | 12-18 | 1.00 | 80-100 | |
| Cucumber | Aug 10-20 | Seed or Plants (2) | 32-36 | 12-30 | .5 to .75 | 60-70 | |
| Eggplant | 15-Jul | Plants | 36 | 18 | - | 80-90 | |
| Pepper | 15-Jul | Plants | 36 | 24 | - | 90-110 | |
| Pumpkin | July 15-30 | Seed or Plants (2) | 36-60 | 30-48 | 1 | 100-120 | |
| Summer Squash | July 15-Sept 1 | Seed or Plants (2) | 36 | 24-36 | 1 | 40-50 | |
| Winter Squash | July 15-30 | Seed or Plants (2) | 36-48 | 30-48 | 1 | 100-120 | |
| Tomatillo | 15-Jul | Plants | 48 | 24-36 | - | 90-100 | |
| Tomatoes | July 1-15 | Plants | 48 | 24-36 | - | 70-90 |
1 = There may be advantages to planting earlier, if soil moisture and climatic conditions are favorable.
2 = Set plants into the garden 1 to 1 1/2 months after planting the seed.
3 = Be vigilant about scouting for fall armyworms in whorl of seedlings and young plants.
* Unless using a cold frame or row covers to extend the season.
Table 2. Semi-hardy vegetables – (may continue to grow and be harvested after several frosts). Many varieties will do well – select varieties that are early maturing and disease resistant.
| Kind | Time to Plant | Method of Planting | Between Rows (inches) | In the Row (inches) | Depth to Cover Seed (inches) | Days From Planting to Harvest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beet | Aug 1-15 | Seed | 12-18 | 3-4 | .5-.75 | 60-70 | |
| Broccoli | July 15-Aug 15 | Plants | 18-30 | 16-20 | - | 70-80 | |
| Brussels Sprouts | July 15-Aug 15 | Plants | 18-30 | 16-20 | - | 90-100 | |
| Cabbage | Aug 1-25 | Plants | 18-24 | 16-20 | - | 75-90 | |
| Chinese Cabbage | Aug 1-25 | Seed or Plants (1) | 12-16 | 10-18 | 0.50 | 75-90 | |
| Carrots | July 15-Aug 15 | Seed | 12-18 | 1-2 | 0.25 | 70-80 | |
| Cauliflower | Aug 1-25 | Plants | 18-24 | 16-20 | - | 70-80 | |
| Collards | Aug 1- Sept 1 | Seed or Plants (1) | 30-36 | 18-24 | 0.50 | 75-85 | |
| Garlic | Sept 1- Oct 15 | Bulbs (cloves) | 12 | 4 | 2 | Early June the following year | |
| Irish Potato | Aug 1-15 | Seed potatoes | 30-42 | 10-16 | 2 | 90-110 | |
| Kale | 1-Sep | Plants | 24-36 | 18 | 0.25 | 50-65 | |
| Kohlrabi | 1-Sep | Plants | 18-24 | 4-6 | 6 | 50-70 | |
| Leaf Lettuce | Aug 1-15 | Seed or Plants (1) | 12-18 | 2-3 | 0.25 | 60-70 | |
| Leek | 1-Sep | Seed or Plants (1) | 12-24 | 2-4 | 0.5 | Late Spring the following year | |
| Mustard | Sept 10 - Oct 10 | Seed | 12-18 | 2-3 | 0.5 | 40-50 | |
| Onions | 1-Sep | Seed, Sets, or Plants (1) | 12-18 | 4 | 0.25 | Late Spring the following year | |
| Parsnip | July 15 - Aug 15 | Seed or Plants (1) | 12-18 | 4-6 | 0.25 | 120 | |
| Peas, green | Aug 15 - Sept 1 | Seed | 36 | 2 | 2 | 60-90 | |
| Radish | Aug 15 - Oct 10 | Seed | 12-Aug | .75-1 | 0.5 | 20-40 | |
| Rutabaga | Aug 15 - Sept 15 | Seed | 24-36 | 3-4 | 0.5 | 80-90 | |
| Spinach | Sept 5-25 | Seed | 8-12 | 1-2 | 0.5 | 50-60 | |
| Swiss Chard | Aug 1 - Sept 15 | Seed | 24-30 | 2-3 | 0.5 | 50-60 | |
| Turnip | Aug 1 - Sept 15 | Seed | 12-124 | 2-3 | 0.5 | 50-60 |
1 = Set plants into the garden 1 to 1 1/2 months after planting the seed.
Note: If planting or sowing into cold frames, plant two weeks later than date indicated. With our abundant winter sunshine, be sure to allow for ventilation. Also, check frequently for pests, especially aphids.
Growing Fall Irish Potatoes
If seed potatoes are available and space permits, potatoes are a desirable supplement to the fall and winter food supply. Yields are usually lower than from spring-planted potatoes, but proper storage is much easier to provide and potato quality is excellent.
The practice of using potatoes from the fresh produce counter for planting purposes is not recommended. This kind of material frequently does not produce adequate growth and is considerably lower in yield.
One of the problems is getting a stand of plants early enough to produce a crop before fall frosts. This emphasizes the need to use matured, medium-to-large potatoes that require cutting into 1 or 1 1/2 ounce size seed pieces.
Cut potatoes should be allowed to cure three to five days before planting, and they should be stored under cool (45° to 65°F) conditions during curing.
In order to have a more favorable (cooler) soil at planting time, deep furrows may be opened in the late afternoon, seed pieces planted, covered with two inches of soil, watered, and mulched with straw or other available organic material. This should provide more favorable conditions for growth.
Harvesting and Storing Vegetables
Vegetables such as carrots, beets, rutabagas, turnips, and Irish potatoes, when harvested, may be stored in a cool, moist location and remain in usable condition until late winter. Place the vegetables in ventilated plastic bags in a cool basement cellar, or “store” them in place in the garden. Once produce reaches maturity, it will “keep” in place through early January. For protection during the cold of December, January, and February, the soil layer over the mound should be six to 10 inches thick. Limited quantities of vegetables may be kept in the refrigerator in order to reduce the problem of frequent removal from the soil mound.
Other crops that produce and store easily include winter squash and pumpkin. These require cool, dry storage conditions.
Recommended reading: “The New Organic Grower’s Four-Season Harvest” by Eliot Coleman, Chelsea Green Publishers.
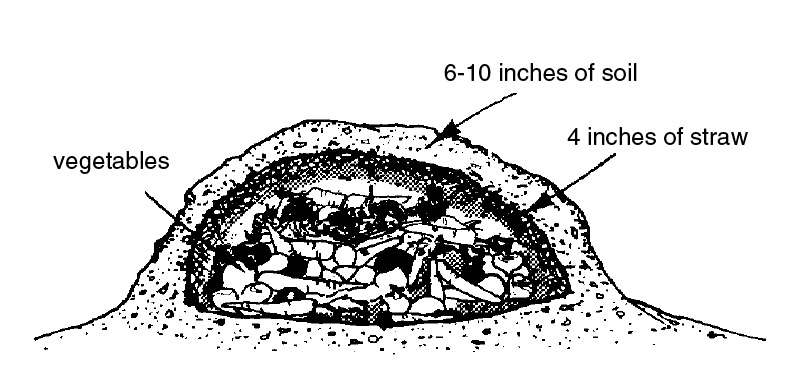
Figure 2. Mound storage of vegetables.
David A. Hillock
Extension Consumer Horticulturist
Brenda Simons
Extension Consumer Horticulturist
