Elements
Nitrogen
Nitrogen (N) is an integral component of amino acids, which are the building blocks for proteins. Proteins in turn are present in the plant as enzymes that are responsible for metabolic reactions in the plant. Because N is so important, plants often respond dramatically to available N.
- General Information
- N has no odor, is tasteless, and colorless.
- Nitrogen gas (N2) makes up 78.1% of the Earth's atmosphere
- Nitrogen is not a metal
- Nitrogen gas is inert. Some soil bacteria can 'fix' nitrogen into a form that plants and animals can use to make amino acids and proteins.
- French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisier named nitrogen azote, meaning without life.
- Nitrogen was sometimes referred to as 'burnt' or 'dephlogisticated' air.
- Nitrogen compounds are found in foods, fertilizers, poisons, and explosives.
- Nitrogen is responsible for the orange-red, blue-green, blue-violet, and deep violet colors of the aurora.
- One way to prepare nitrogen gas is by liquefaction and fractional distillation from the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen has a valence of 3 or 5.
- Atomic Number: 7
- Atomic Mass: 14.0067
- Physical properties of Nitrogen
- Boiling Point at 1atm: -195.8°
- Freezing Point at 1atm: -209.9°
- Density of the gas at 21.1° and 1atm: 1.153 kg/m3
- Uses of Nitrogen
Nitrogen finds use in diverse commercial applications, including:
- Chemical Processing: to inert vessels and oxygen-sensitive chemicals, creating an oxygen-deficient environment that reduces safety hazards; to propel liquids through pipelines; and to manufacture ammonia.
- Food: to extend shelf-life in packaged foods by preventing spoilage from oxidation, mold growth, moisture migration and insect infestation; to rapidly freeze; and to refrigerate perishables during transport.
- Petroleum Recovery and Refining: to improve recovery and maintain pressure in oil and gas reservoirs; to blanket storage tanks and product loading/unloading; to purge pipelines; and to strip volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from waste streams or to cool vent streams. Controlling VOC emissions helps refiners comply with U.S. Clean Air Act requirements.
- Metal Production and Fabrication: to protect metals such as steel, copper and aluminum during annealing, carburizing and sintering operations in high temperature furnaces; to cool extrusion dies; and to shrink fit metal parts; utilized as a purge gas with stainless steel tube welding. Also used to support plasma cutting.
- Electronics: to prevent oxidation in the manufacture of semiconductors and printed circuits; and to enhance solvent recovery systems by eliminating the use of chlorofluorocarbons for cleanup.
- Glass Manufacturing: to cool furnace electrodes and prevent oxidation during manufacturing; and to lower air temperatures for optimum cooling rates.
- Research and Health Services: to freeze and preserve blood, tissue, semen and other biological specimens; to freeze and destroy diseased tissue in cryosurgery and dermatology; and to pre-cool or insulate Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), conserving the more costly helium.
- Construction: to suppress the pour temperature of concrete mixtures, inhibiting the formation of cracks; and to stabilize the ground as in the restoration of the Leaning Tower of Pisa.
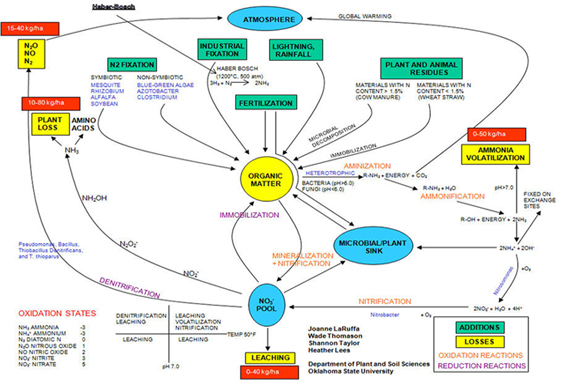
- Cycle
- Fertilizers
Nutrient Content, %
Source N P2O5 K2O CaO MgO S Cl Form Anhydrous ammonia 82 gas Aqua ammonia 20-25 liquid Ammonium chloride 25-26 66 solid Ammonium nitrate 33.5 solid Ammonium sulfate
21-0-0-2421
24solid Monoammonium phosphate
MAP 10-52-011 48-55 2 0.5 1-3 solid Diammonium phosphate
DAP 18-46-018-21 46-54 solid Ammonium phosphate-sulfate 13-16 20-39 3-14 solid Ammonium polyphosphate
APP 10-34-010-11 34-37 liquid Ammonium thiosulfate 12 26 liquid Calcium nitrate 15 34 solid Potassium nitrate 13 44 0.5 0.5 0.2 1.2 solid Sodium nitrate 16 0.6 solid Urea 46 solid Urea-sulfate 30-40 6-11 solid Urea-ammonium nitrate (UAN) 28-32
liquidUrea-ammonium phosphate 21-38 13-42 solid Urea phosphate 17 43-44 solid Further Information: 1 gallon of 32-0-0 contains 3.54 lbs. of N and weighs about 11.1 lbs. 1 gallon of 28-0-0 contains 2.99 lbs. of N and weighs about 10.7 lbs. 1 gallon of 82-0-0 contains 4.25 lbs. of N and weighs about 5.2 lbs.
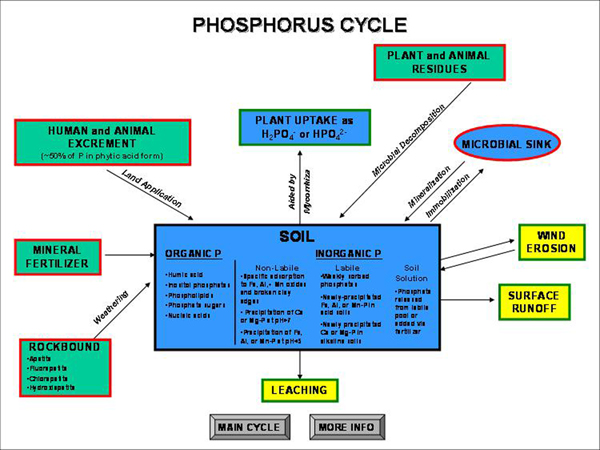
Phosphorus
Most of the total phosphorus in soils is tied up chemically in compounds with low solubility. In neutral to alkaline pH soils, calcium phosphates are formed, while in acid soils, iron and aluminum phosphates are produced.
- General Information
- Phosphorus is a immobile nutrient. This being so the need is not related to yield to rather related to concentration in the soil. When a soil test is returned the analysis whether reported in ppm, STP, or lbs per ac is related to the sufficiency of P in the soil.
- As a note STP as reported by OSU SWFAL is essentially lbs/ac. PPM *2 equals lbs/ac of a 6" soil sample.
Soybeans Wheat Corn Soil test P Percent Sufficiency P2O5 lb/ac Percent Sufficiency P2O5 lb/ac Percent Sufficiency P2O5 lb/ac 0 40 70 50 80 40 80 10 60 50 70 60 65 60 20 80 30 80 40 80 40 40 95 20 95 20 95 20 65 100 0 100 0 100 0 - Cycle
- Fertilizers
Nutrient Content, %
Source N P2O5 CaO MgO S Form Monoammonium phosphate MAP 10-52-0 11 48-55 2 0.5 1-3 solid Diammonium phosphate DAP 18-46-0 18-21 46-54 solid Ammonium phosphate-sulfate 13-16 20-39 3-14 solid Ammonium polyphosphate APP 10-34-0 10-11 34-37
liquidUrea-ammonium phosphate 21-38 13-42 solid Urea phosphate 17 43-44 solid Ordinary Super-phosphate 16-23 solid Conc. Triple Super-phosphate TSP 0-46-0 44-53 solid Rock phosphate 25-50 solid
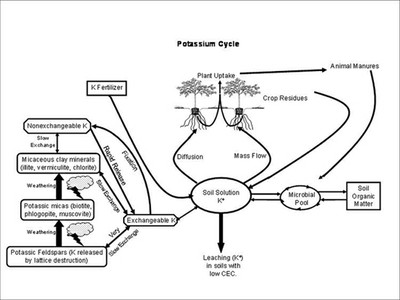
Potassium
Plants take up potassium as the potassium ion (K+). Potassium within plants is not synthesized into compounds and tends to remain in ionic form in cells and plant tissue. Potassium is essential for photosynthesis, starch formation and translocation of sugars within plants. It is necessary for the development of chlorophyll, although it is not part of its molecular structure.
The main functions of potassium in plants are in the translocation of sugars and its involvement in photosynthesis.
- General Information
Potassium is a relatively immobile nutrient. This being so the need is not related to yield to rather related to concentration in the soil. When a soil test is returned the analysis whether reported in ppm, Soil Test K, or lbs per ac is related to the sufficiency of P in the soil.
Potassium is mobile in the Plant so deficiencies will appear in lower leaves as yellowing around the out edges.
As a note Soil Test K as reported by OSU SWFAL is essentially lbs/ac. PPM *2 equals lbs/ac of a 6" soil sample.
- Severe K Deficiency in soybeans
Severe K deficiency was observed in soybean plant in North Central to North Eastern OK in the summer of 2009. Most of these fields were planted wet (which created compaction and poor root growth), had experience a expend cool wet period (reducing K availability and uptake), and had very low Soil Test K levels. Once the warm weather hit the bean took off and the roots and soil could not support the growth. Note lower leaves show the decency, new leave are green.
- Special Considerations
K under Drought Conditions:
Potassium deficiencies can be induced by dry soil conditions. Potassium is taken up by plant primarily through the process of diffusion into the roots. This process is facilitated by water, in drought conditions the film of water that surrounds the roots becomes too thin and the plant has difficulty pulling K into the root.
Much of the fields that show K deficiency symptoms in Oklahoma in dry periods are often fields that also have low to moderate Soil Test K levels. This brings out two points, the dry weather increases the impact of the low soil K levels and that a application of K fertilizer may have prevented the issue.
An additional note is that Drought induced K deficiencies do not also exhibit the Classic K symptomology. In a few cases the deficiencies will develop in the middle of the plant, not on the oldest leaves as typically seen but also not on new growth.
Correcting the Problem
Correction of drought induced K deficiency lies in prevention. During the dry period very little can be done. Once crop receives rain and soil moisture is replenished deficiencies will be corrected. Since K is mobile in the plant (why symptoms develop on old leaves) the yellowing will never go away.
As mentioned Soil testing and proper pre-plant fertility will diminish the likelihood of experiencing this problem.
- Cycle
- Fertilizers
Nutrient Content, %
KTS Density, lbs/gallon @ 60ºF = 12.2Source N P2O5 K2O S Form Potassium Chloride (Muriate of Potash) 60 solid Potassium Sulfate 50 17 solid Pottasium ThioSulfate (KTS) 25 17 liquid