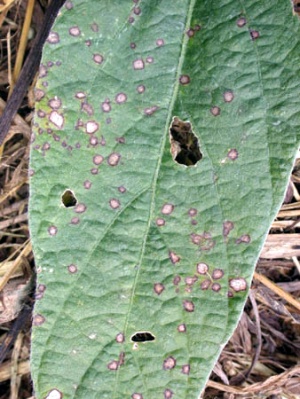
Frogeye Leaf Spot
 Causal Agent
Causal Agent
Cercospora sojina, a fungus
Hosts
Soybeans.
Symptoms
This disease is most severe during years with above average rainfall and high relative humidities. Young leaves are extremely susceptible while older leaves are more resistant. However, because visible lesions do not develop until 10 to 14 days after infection, young leaves never exhibit symptoms of frogeye leaf spot.
On older leaves the lesions measure up to ¼ inch in diameter but may coalesce to form larger spots. Young, fully developed lesions have a gray to brown center with a distinct purple to reddish margin. As lesions age, the center becomes nearly white, and the margins darken.
Control
Control of frogeye leaf spot is obtained through the use of crop rotation, plowing down old soybean debris, and the use of resistant varieties. Varieties susceptible to frogeye leaf spot can be protected by applying foliar fungicides. Fungicides should be applied at late flowering (R3) and beginning seed growth (R4) to protect against frogeye infections. However, most years frogeye does not reach severe enough infections levels to support the use of foliar fungicides. Please contact your local county extension office for current information.