Asparagus Culture in the Home Garden
Asparagus is one of the more expensive vegetables to purchase, whether canned, frozen, or fresh; but few vegetable crops in Oklahoma are easier to grow or more consistent in production.
One of the earliest spring vegetables to be harvested, asparagus is an excellent source
of substantial quantities of minerals and vitamins.
Asparagus (Asperagus officinalis) is a hardy perennial plant, which produces edible stems (spears). Plants may grow
to a height of four to eight feet and are branched. Although native to central Asia,
it is grown throughout the world. For more than 2,000 years, it has been cultivated
and used for food and medicine. Early colonists brought it to America as seed. It
is now grown in most states and Canadian provinces.
Varieties
The most commonly available varieties are Mary and Martha Washington. Asparagus rust sometimes becomes a problem due to cool, wet weather. These varieties have limited resistance to this disease.
Climate
Asparagus requires a dormant period during which considerable chemical change takes place in the reserve food supply stored in the roots. Winter conditions in Oklahoma are sufficient to allow these chemical changes to take place.
Soil Preparation
Since asparagus plants remain vigorous and productive for as long as 15 years, it’s
worth the time to correctly and thoroughly prepare the soil with the necessary organic
matter and fertilizer before planting. Asparagus can be grown on many kinds of soil,
but sandy-loam soils with a less porous-type subsoil are best. Good drainage is essential.
Add to your sandy loam soil two to four inches of organic matter. Incorporate this
into the soil to a depth of six to eight inches. Add commercial fertilizer as needed.
(Determine kind and amount by a soil test.)
Make annual applications of commercial fertilizer as indicated by soil tests, plant
growth, and production. This might be in the range of one-half to one pound of actual
nitrogen per 50 feet of row and applied broadcast in early March. A similar amount
may be applied following harvest. This will stimulate top growth, resulting in more
food produced and stored for next year’s productions.
In soils slightly to moderately acid (pH 6.5-5.5), applications of agricultural limestone
may be very beneficial. Broadcast four to eight pounds of agricultural limestone per
50 feet of asparagus row. One application may be sufficient for two or three years,
depending on rainfall and soil tests.
Seedlings
If you desire, you may produce one-year-old crowns by planting seeds in April and growing the seedlings for one year prior to digging and planting in a permanent row location.
When strong one-year-old crowns are used, each established plant will produce approximately
one pound of edible asparagus during the full harvest season. There are many instances
when the production will be greater than this; but this is an average. This will provide
a guide to the number of plants and the space required, based upon individual requirements.
Planting
Asparagus may be grown as individual plants in a row in the garden or as clumps in the yard. Locate the planting on the side of the garden where it will least interfere with other gardening activities.
Planting may be done during the late fall, winter, or early spring. Plant growth is
greatly influenced by adequate soil moisture. Good fern growth one year can result
in high yields the following season.
Select a sunny location where there is a minimum of competition from the roots of
trees and shrubs. Use one year-old asparagus crowns for planting.
Place the crowns approximately six to eight inches deep, 18 inches apart in the row, with the rows four to five feet apart (Figure 1). In heavier soils, it may be best to set plants no more than four inches deep. When properly grown, the plants have a very extensive root system. Dig the holes large enough and deep enough that the roots of the plant can be spread out properly and allowed to grow normally.
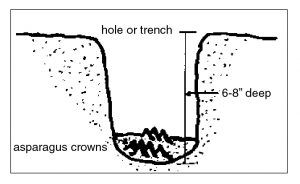
Figure 1
Cover the crowns with two or three inches of soil (Figure 2). Allow the soil to settle
around the plants. Continue filling later in the year, after growth has begun (Figures
3 and 4). This accomplishes two things: 1) it covers up small grass and weed plants
down in the hole or trench and 2) it allows asparagus to develop more extensively
than it would if it were to grow through six to eight inches of soil in the very beginning.
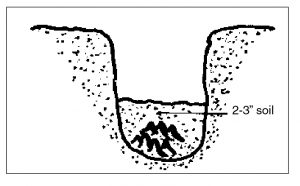
Figure 2
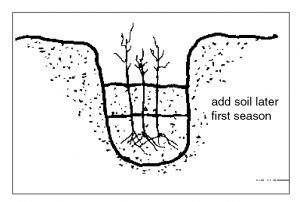
Figure 3
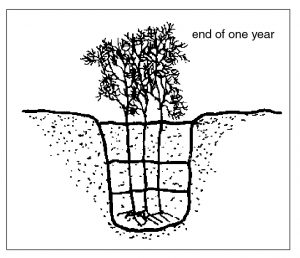
Figure 4
Growth and Harvesting
The quantity and quality of asparagus produced depend on the amount of food stored in the plant’s roots and crowns from the previous season of growth. This is why it is so important to allow the plant to become well established the first season without any harvest. Plants need to develop to a large size in order to produce an abundance of stored food.
Start harvesting with the third year. Harvest only as long as a quantity of stored
food in the crown will permit. You may harvest until the diameter of the newly emerging
spears is small—perhaps 3/8″ in diameter. This indicates the total amount of stored
food remaining in the crown is rather limited. Do not harvest anymore. This will allow
the plant to produce foliage and manufacture food for adequate production the following
year.
Length of Harvest Season
A dry season, a lack of sufficient fertilizer, competition by grasses and weeds, plants spaced too closely, or shaded too much are factors that can materially reduce the length of the harvest period as well as the total yield. The following suggested length of harvest season is at best approximation:
- First summer–no harvest
- Second summer–harvest two to three weeks
- Third summer–four to six weeks
- Fourth and succeeding summers–eight to twelve weeks. (If the plants have not been properly grown, the length of the harvest season might be only half as long as otherwise suggested.) Rather than using a given number of weeks, however, it is best to rely on the plant itself, using the size of the spears to determine the length of harvest.
Harvesting Methods
Harvest in the early spring as the first spears appear and continue to harvest all the spears for the entire harvest period. If the very small spears are not removed during harvest, there may be fewer new spears produced, thus a reduction in total yield. Sufficient top growth on the plant usually stops further spear production.
The best time to harvest is during the morning when the stems or spears are crisp
and turgid. They snap more easily and usually contain less fiber.
A spear should be five to seven inches long when harvested. Snap or break the spears
slightly above the ground. A spear that is bent over breaks or snaps at the base of
the succulent portion of the stem and leaves the fibrous portion in the earth.
Refrigerate harvested asparagus spears as soon as possible. Room temperature storage
will cause them to develop toughening fibers and lose nutritive value.
David Hillock
Consumer Horticulture Specialist
