Plant Health Update, September 2025 Summary
In the early part of 2025, many trees developed a large canopy due to abundant rainfall and moderate temperatures. By late summer (August, September), the temperatures were generally above average, and many areas of the state were on the dry side. These weather conditions are conducive for the expression of bacterial leaf scorch disease symptoms, and samples were submitted to the PDIDL from many areas of central Oklahoma during September. As symptoms of bacterial leaf scorch can be confused with marginal discoloration due to drought and high temperatures, a diagnosis requires laboratory testing.
Bacterial leaf scorch is caused by Xylella fastidiosa. Although the bacterium is found throughout the US and includes hundreds of hosts, the number of reported hosts in Oklahoma is limited (Table 1).
| Common Name | Latin Name |
|---|---|
| American elderberry | Sambucus canadensis |
| American elm | Ulmus americana |
| American sycamore | Platanus occidentalis |
| Bermudagrass | Cynodon dactylon |
| Giant ragweed | Ambrosia trifida |
| Grapes | Vitis spp. |
| Hop clover | Trifolium campestre |
| Mulberry | Morus spp. |
| Oak | Quercus spp. |
| Porcelain berry | Ampelopsis brevipedunculata |
| Wood sorrel | Oxalis spp. |
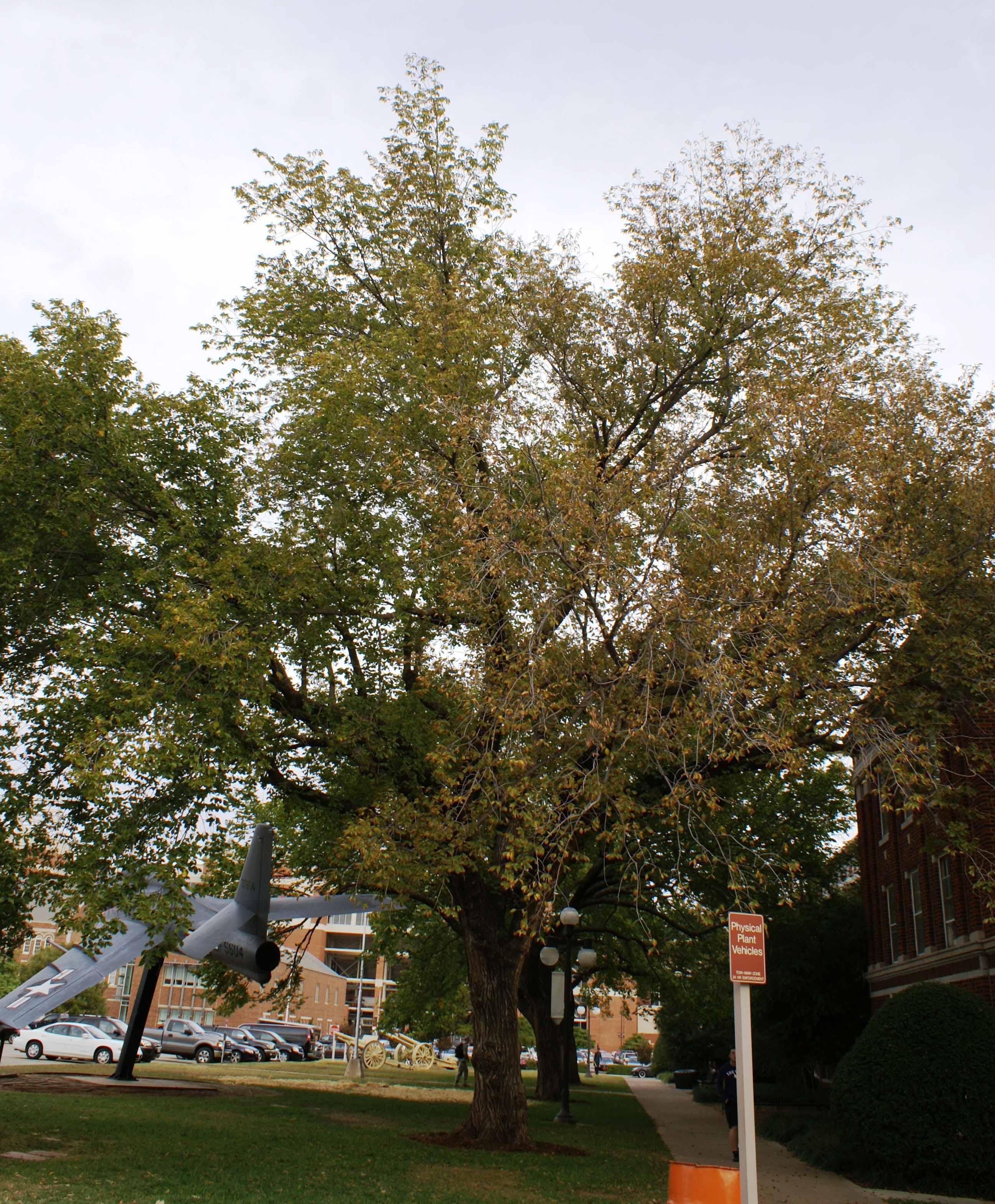
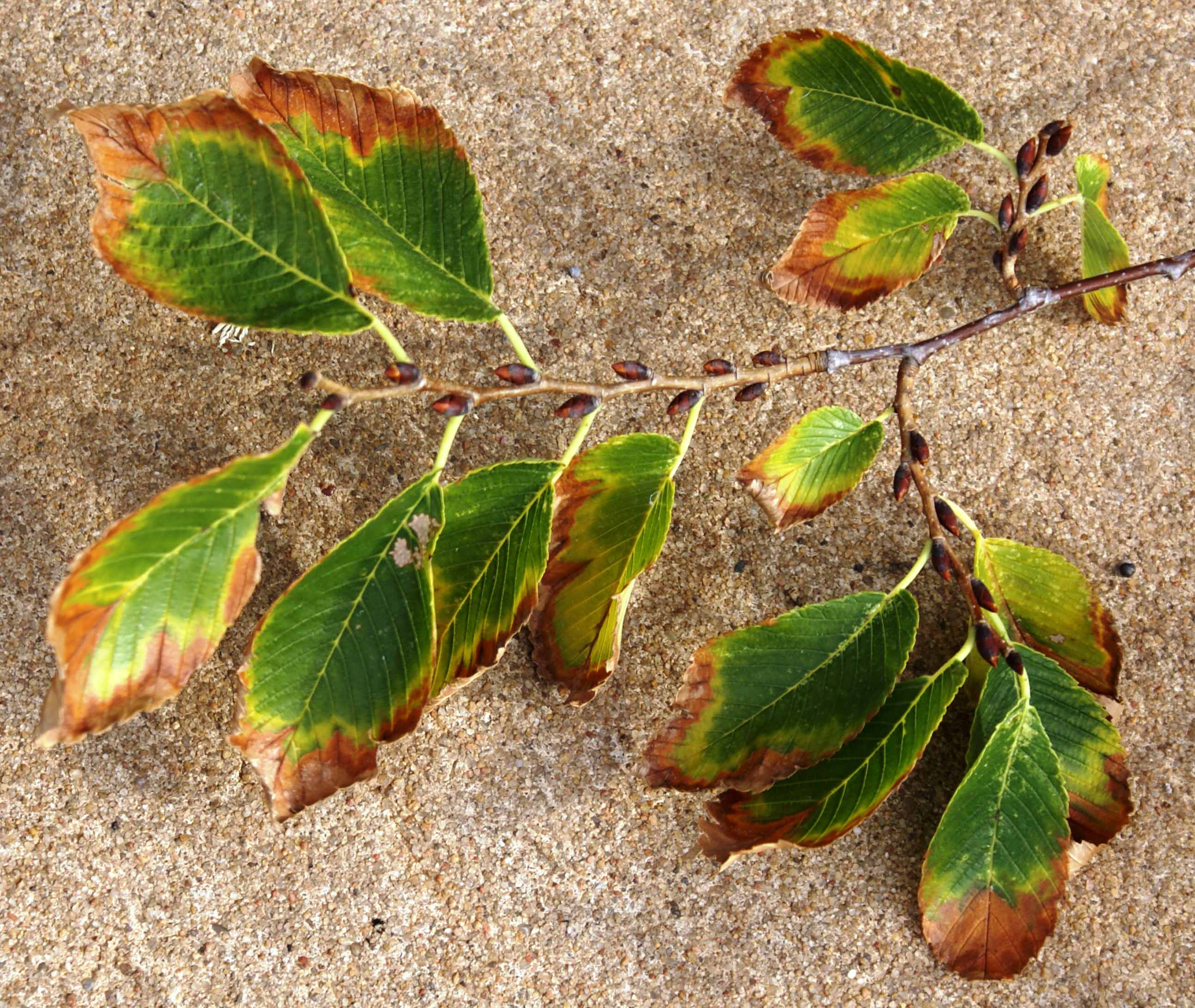
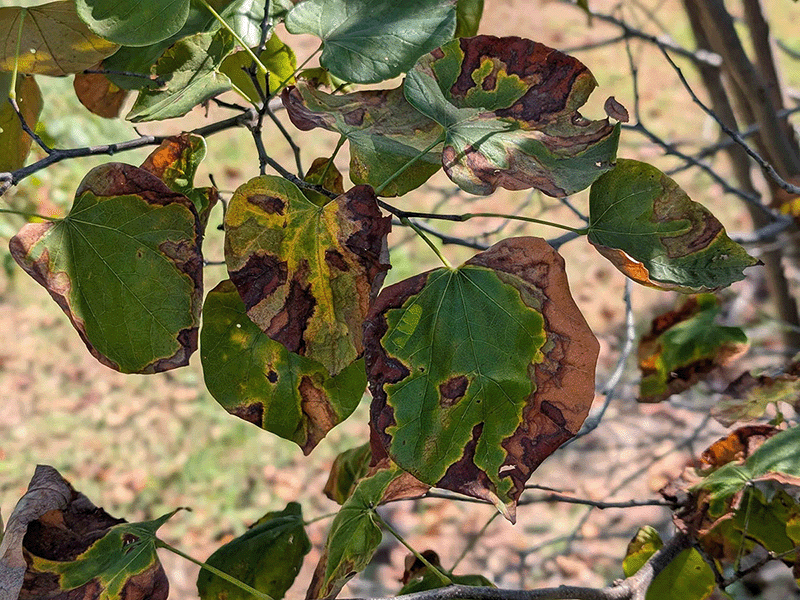
Infected trees develop yellowing and browning foliage from late summer to early fall (Figure 1). Close inspection of affected leaves shows that the margins are brown, and a yellow halo is generally present in the transitional zone between brown and green (Figure 2). Perennial and woody plants show progressive decline, and the disease is eventually fatal.
Figure 1. American elm with premature yellowing and browning of leaves due to bacterial leaf scorch disease. Image taken in early September.
Figure 2. Typical marginal discoloration (browning and yellowing) of American elm leaves with bacterial leaf scorch.
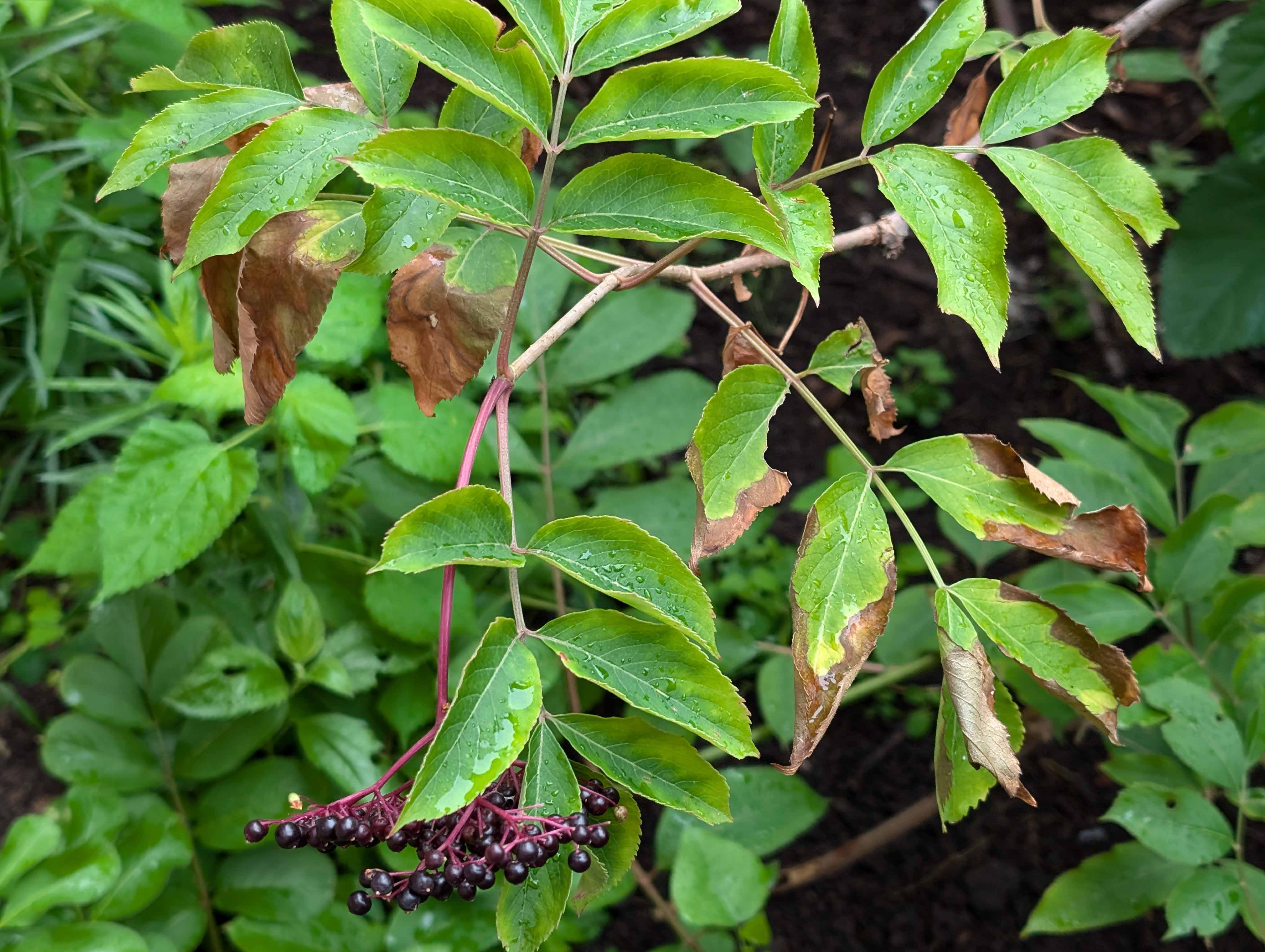
In 2024, an American elderberry with bacterial leaf scorch symptoms was observed in Payne County, Oklahoma (Figure 3). Symptomatic leaves were tested by the PDIDL and found positive for X. fastidiosa. This was a first report for the bacteria affecting this host and it was published in November 2025.
Figure 3. American elderberry with marginal leaf discoloration due to bacterial leaf scorch disease.
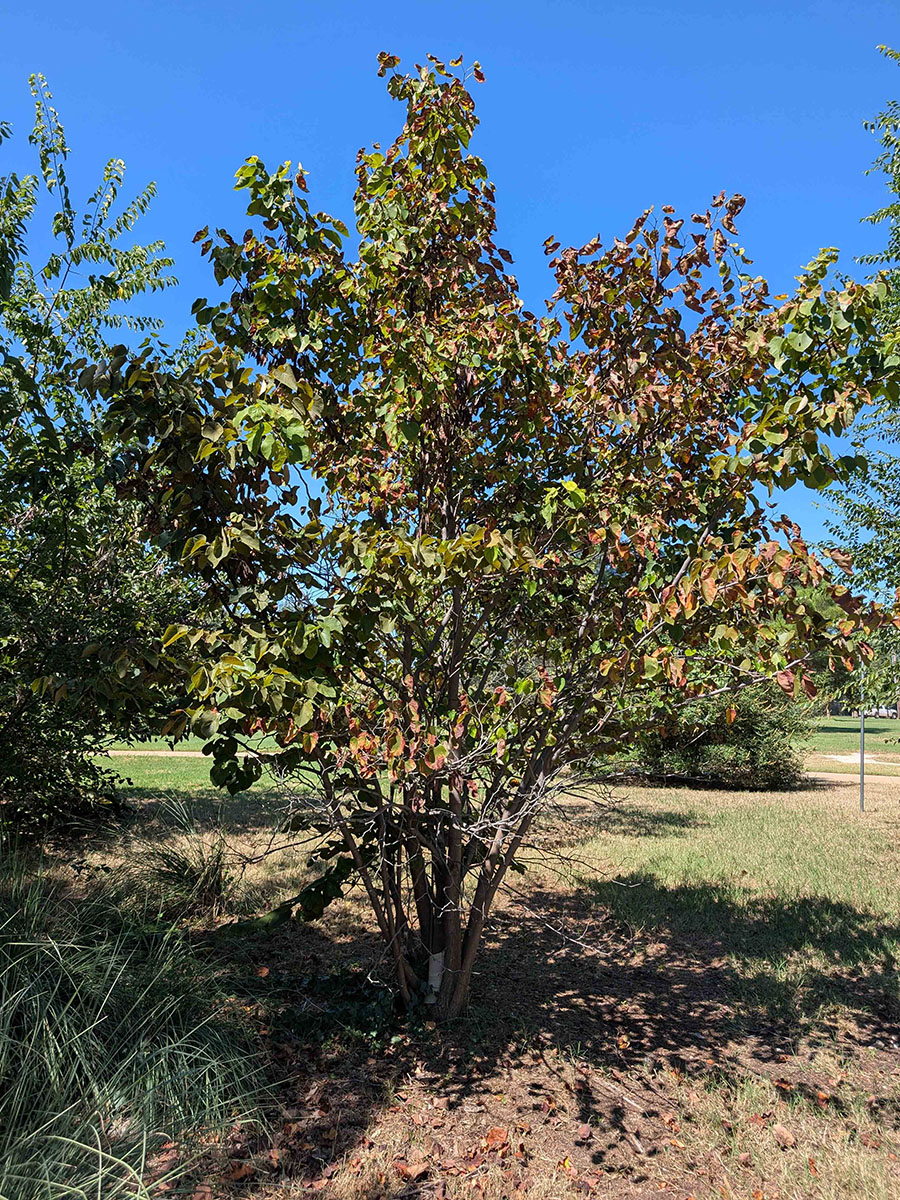
In September 2025, symptoms of bacterial leaf scorch were observed on an Eastern redbud (Cercis candensis) in Oklahoma City (Figure 4). The tree exhibited premature defoliation and marginal leaf discoloration (Figure 5).
Figure 4. Eastern redbud in Oklahoma City with yellowing and browning of leaves due to bacterial leaf scorch. The disease also causes premature defoliation and branch dieback.
Figure 5. Marginal browning and yellowing of Eastern redbud leaves due to bacterial leaf scorch disease.
There is no cure for bacterial leaf scorch disease, and the disease can be spread by xylem-feeding insects. The insects may spread the bacteria to other plants in the area when they feed on infected plants. Both American elderberry and Eastern redbud are native plants in Oklahoma. Pecan trees are also hosts of this bacterium. To date, the disease has not been found to affect pecans in Oklahoma, although it is found in nearby states (Louisiana, Texas). Recognizing new hosts allows growers to better scout unmanaged areas around orchards for potential bacterial leaf scorch symptoms. Elimination of any plants harboring the disease can prevent its spread into pecan orchards. This practice is already employed by grape growers since the bacterium has been found in grape vineyards in our state.
A summary of all submissions in September to the PDIDL by Oklahoma specialty crop growers is provided in Table 2. Look for additional plant health updates from the PDIDL in the next few weeks for our remaining 2025 submissions. If you have suggestions for future topics, please contact jen.olson@okstate.edu or call the PDIDL at (405) 744-9961.
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
|---|---|
| DD | Digital Diagnosis |
| M | Microscopy |
| S | Serological tests |
| C | Culture analysis |
| N | Nematode analysis |
| MD | Molecular diagnostic methods |
| DS | DNA sequencing |
| RS | Referral to specialist |
| O | Other |
| Number | Host | Diagnosis/Identification | County | DD | M | S | C | N | MD | DS | RS | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple | Canker (Neofusicoccum parvum) | Cherokee | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 2 | Apple | Environmental stress, insect damage | Tulsa | X | ||||||||
| 3 | Apple | Suspect Japanese beetle feeding damage | Tulsa | X | ||||||||
| 4 | Apple | Undetermined problem | Ottawa | X | ||||||||
| 5 | Apple | Roots or trunk problem suspected | Craig | X | ||||||||
| 6 | Arborvitae | Environmental stress | Logan | X | ||||||||
| 7 | Arborvitae | Environmental problem; secondary organisms | Cherokee | X | X | |||||||
| 8 | Ash | Spider mite damage suspected | Wagoner | X | ||||||||
| 9 | Azalea | pH induced pathology | Tulsa | X | ||||||||
| 10 | Basil, Sweet | Green lynx spider (Peucetia viridans) | Payne | X | ||||||||
| 11 | Basil, Sweet | Leaf spot (suspected abiotic) | Cleveland | X | X | X | ||||||
| 12 | Bermudagrass | Environmental problem | Canadian | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 13 | Bermudagrass | Animal urine damage suspected | Garfield | X | ||||||||
| 14 | Blueberry | Environmental stress | Payne | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 15 | Boxwood | Branch dieback (likely winter injury) | Payne | X | ||||||||
| 16 | Cactus | Non-pathogenic fungi, Saprophytes | Tulsa | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 17 | Catmint | Bumblebee moth | Canadian | X | ||||||||
| 18 | Cedar, Blue Atlas | Cultural problem suspected | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 19 | Cherry, Weeping | Green stink bug | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 20 | Chestnut | Environmental stress | Tillman | X | ||||||||
| 21 | Crape myrtle | Crape myrtle bark scale | Payne | X | ||||||||
| 22 | Cypress | Seasonal needle drop | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 23 | Cypress (Taxodium sp.) | Pneumatophores (knees) | Wagoner | X | ||||||||
| 24 | Daisy, Shasta | Crown gall | Tulsa | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 25 | Dogwood | Various arthropods (mites, scales) | Payne | X | ||||||||
| 26 | Dogwood | Bot canker (Botryosphaeria dothidea) | Payne | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 27 | Elm | Bacterial leaf scorch (Xylella fastidosa) | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 28 | Elm | Canker (Botryosphaeria dothidea) | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 29 | Elm | Bacterial leaf scorch (Xylella fastidosa) | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 30 | Elm | Elm leaf beetle | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 31 | Elm | Wound canker | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 32 | Elm | Native elm wilt, Hypoxylon canker | Payne | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 33 | Elm | Native elm wilt, Bot canker, Elm lace bugs | Payne | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 34 | Elm, American | Canker and decline (Dothiorella sp.) | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 35 | Elm, American | No pathogen detected | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 36 | Fescue | Weed ID-Foxtail, Setaria sp. | Craig | X | ||||||||
| 37 | Fir | Cytospora canker suspected | N/A | X | ||||||||
| 38 | Garden | Whiteflies | Kay | X | ||||||||
| 39 | Garden | Black and yellow Argiope spider | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 40 | Garden | Yellow woollybear | Okfuskee | X | ||||||||
| 41 | Garden | Skimmers (Family Libellulidae) | N/A | X | ||||||||
| 42 | Garden | Black and yellow Argiope spider | Osage | X | ||||||||
| 43 | Grass, Ornamental | Fungal leaf spot suspected | Grady | X | ||||||||
| 44 | Hibiscus | Rhizoctonia and Fusarium stem rot | Cherokee | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 45 | Hibiscus, Common | No pathogen found | Washington | X | ||||||||
| 46 | Hibiscus, Common | Normal plant growth | Washington | X | ||||||||
| 47 | Hollyhock | Hollyhock rust | Logan | X | ||||||||
| 48 | Horse Chestnut | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 49 | Hydrangea | Cercospora leaf spot suspected | Garfield | X | ||||||||
| 50 | Hydrangea, Panicle | Rhizoctonia root rot | Cherokee | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 51 | Ironwood, Persian | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 52 | Juniper | Environmental stress, secondary fungi | Muskogee | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 53 | Juniper | Environmental problem | Kay | X | ||||||||
| 54 | Juniper | Site related problem suspected | Texas | X | ||||||||
| 55 | Lavender | Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporum) | Rogers | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 56 | Linden, Japanese | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 57 | Linden, Little Leaf | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 58 | Magnolia | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 59 | Maple | Spider mites | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 60 | Maple | Leaf spot (Collectotrichum) | Tulsa | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 61 | Maple | Maple aphid (Drepanaphis sp.) | Cleveland | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 62 | Maple. Japanese | Insect feeding damage | Muskogee | X | X | |||||||
| 63 | Maple, Silver | Mushroom (unidentified fungus) | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 64 | Maple, Sugar | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 65 | Milkweed | Milkweed tussock moth | Murray | X | ||||||||
| 66 | Mulberry | Fungal leaf spot suspected | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 67 | Mulberry | Bacterial leaf scorch (Xylella fastidosa) | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 68 | Mulberry | Cercospora leaf spot suspected | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 69 | Ninebark | Cercospora leaf spot | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 70 | Oak | Spink oak slug caterpillar | Craig | X | ||||||||
| 71 | Oak | Environmental stress | Grady | X | ||||||||
| 72 | Oak | Bacterial leaf scorch, Cytospora canker | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 73 | Oak | Tubakia leaf spot suspected | Wagoner | X | ||||||||
| 74 | Oak | Hypoxylon canker suspected | Kay | X | ||||||||
| 75 | Oak | Sunscald | Okmulgee | X | ||||||||
| 76 | Oak | Environmental stress | Okfuskee | X | ||||||||
| 77 | Oak | Lightning injury | Noble | X | ||||||||
| 78 | Oak, Black-jack | Tubakia leaf spot, Spider mites | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 79 | Oak, Bur | Slime mold suspected | Logan | X | ||||||||
| 80 | Oak, English | Lower down problem suspected | Washington | X | X | |||||||
| 81 | Oak,English | Lower down problem suspected | Washington | X | ||||||||
| 82 | Oak, English | Lower down problem suspected | Washington | X | X | |||||||
| 83 | Oak, Sawtooth | Endothia canker, Discula antracnose | Canadian | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 84 | Oak, Shumard | Branch dieback (unidentified cause) | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 85 | Oak, White | Animal damage | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 86 | Okra | Normal plant growth | Tulsa | X | ||||||||
| 87 | Palm, Ponytail | Thrips | Pontotoc | X | ||||||||
| 88 | Pear | Fire blight (Erwinia amylovora) | Payne | X | X | |||||||
| 89 | Pear | Fire blight (Erwinia amylovora) | Cherokee | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 90 | Pecan | Pecan scab | Tulsa | X | ||||||||
| 91 | Pecan | Spider mites, environmental problems | Cleveland | X | X | X | ||||||
| 92 | Pecan | Woodpecker damage | Wagoner | X | ||||||||
| 93 | Pecan | Environmental stress | Tillman | X | ||||||||
| 94 | Pecan | Branch and twig borer (Family Bostrichidae) | Tulsa | X | ||||||||
| 95 | Pecan | Honey mushrooms (Armillaria tabescens) | Tulsa | X | X | X | ||||||
| 96 | Pecan | Wood rot (Schizophyllum commune) | Tulsa | X | X | X | ||||||
| 97 | Peony | Peony leaf spot (Cladosporium) suspected | Garfield | X | ||||||||
| 98 | Pepper | Sunscald | Pontotoc | X | ||||||||
| 99 | Pepper | Herbicide injury | Garfield | X | X | X | ||||||
| 100 | Pine | Season needle drop; Dothistroma needle blight | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 101 | Pistache, Chinese | Environmental problem suspected | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 102 | Plant ID request | Native grass (Tridens oklahomensis) | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 103 | Redbud, Eastern | Sunscald | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 104 | Redbud, Eastern | Bacterial leaf scorch (Xlyella fastidosa) | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 105 | Redbud, Eastern | Canker (unidentified cause) | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 106 | Redbud, Eastern | Abiotic scorch, suspected | McClain | X | ||||||||
| 107 | Rose | Root problem suspected | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 108 | Rose | Crown canker suspected | Okmulgee | X | ||||||||
| 109 | Roselle | Canker (Botryosphaeria dothidea), Stem spots (Cercospora sp.) | Payne | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 110 | Rudbeckia | Rust | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 111 | Sedum | Environmental problems | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 112 | Seven Sons Flower | Environmental problems | Payne | X | X | |||||||
| 113 | Shumard oak | Alcoholic flux | N/A | X | ||||||||
| 114 | Smoke tree | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 115 | Spirea | Environmental stress | Oklahoma | X | X | |||||||
| 116 | Squash | Melon aphid (Aphis gossypii) | Washita | X | ||||||||
| 117 | Strawberry | Black root rot complex (Rhizoctonia, Fusarium) | Tulsa | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 118 | Tree | Slime mold | McClain | X | ||||||||
| 119 | Tree | Unidentified mushroom | Okfuskee | X | ||||||||
| 120 | Turfgrass | Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) | Cleveland | X | ||||||||
| 121 | Turfgrass | Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) | Payne | X | ||||||||
| 122 | Vinca | Phytopthora blight and root rot (Phytophthora nicotianae) | Cleveland | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 123 | Watermelon | Fruit spot (unidentified agent) | Oklahoma | X | ||||||||
| 124 | Willow | Rhizoctonia root rot | Cherokee | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 125 | Zinnia | Virus suspected | Payne | X | ||||||||
| 126 | Zinnia | Tospovirus | Payne | X | X | |||||||
| 127 | Zinnia | Tospovirus | Logan | X | X | X | ||||||
| 128 | Zinnia | Tospovirus | Cleveland | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 129 | Zinnia | Tospovirus | Cleveland | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 130 | Zinnia | Tospovirus group | Oklahoma | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 131 | Zinnia | Powdery mildew | Cleveland | X |